Photographers the world over know the late afternoon light. The warm glow, the soft slanting shadows, the delicate glancing sheen that brings everything alive. In Bangla, this light has a special name. kone dekhano alo [the light for showing off the bride.] Apart from the universal issues of brides being seen as commodities, and of marriage being a social spectacle, it speaks of how the environment in which things are displayed, reflects upon what is displayed. Photographs are visual representations. Exhibitions are collective displays of photographs. Festivals are displays of exhibitions. Within this biennial Chobi Mela is a display of a festival. At each level, the alo [light] that we use to display the festival, the exhibition, the print, has a bearing on how we see it.
[wpvideo TJhz2x0N]
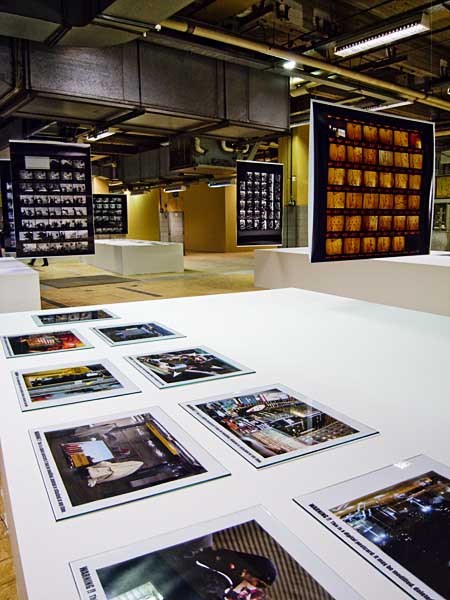
Setting up the show. 16th October 2008. ? Shahidul Alam/Drik/Majority World
The choices made as the photograph is taken, as an exhibition is put together, as a festival is assembled, as a biennial is visualized, take into account the way each entity will be perceived by the intended audience. The relationship between the viewer and the viewed. This is impossible to pre-visualize at the moment of photography. So there are several authors who play with this alo. The political space within which an exhibition operates is tempered by the tertiary meaning that a festival director imparts, in choosing to display a body of work. In determining how it is shown, and how it relates to other work on display. The alo is not static. A festival put together when the world witnesses unjust war and an illegal occupation, will be seen differently from a festival that is viewed at a time of peace. The same exhibitions (though exhibitions are never the same and change with each displacement), seen in a different venue, nation or continent, with different proximities to zones of tension, will change in meaning even when the images remain the same. Relocating a festival allows further interpretations. So what alo do we use for showing off this festival?
[wpvideo EyyfuMFl]
Artistic Director of Brussels Biennial Barbara Vanderlinden introducing show to artists and curators 18th October 2008. ? Shahidul Alam/Drik/Majority World
Chobi Mela was conceived in a nation that was far removed from the established capitals of photography. Bangladeshi photographers did not feature in the classical books on this medium. The images of Bangladesh seen worldwide were images produced largely by white western photographers. There had been no festival of photography in Asia. In much of Asia and most of the majority world, photography is not considered an art form. So several issues were being tackled. The ignorance about non-western photographic practice (this was true even within Bangladesh, where photographers knew about Ansel Adams and Edward Weston, but were unaware of important work being done in neighboring countries.) The non-recognition of photography as a valid profession and an art form. The limited opportunities that Bangladeshi and regional photographers had of seeing photography.

There was another significant but very localized goal. In a nation where the majority of people cannot read or write, photography provided one of the few means through which ordinary people could be reached. As the festival migrates to Brussels, several of these goals diminish in importance. Others, however, take on greater relevance. An ignorance of photographic practice outside Europe and North America is perhaps a greater ailment in Brussels than it is in Dhaka. A critique of western lifestyles is perhaps of greater importance to Europeans. An understanding of majority world cultures outside their stereotypical representation in the West is certainly a more crying need in a culture fed largely on fast-food photography.

There are commonalities too. Belgium is in a state of flux with internal tensions that threaten to divide the nation. Bangladesh also has its internal politics of dominance, and the power struggles between the major political parties have taken it to the brink of civil war. While the show goes on in Brussels, Bangladesh will continue to be in a state of emergency with fundamental freedoms curtailed. The streets of Dhaka were in flames while Chobi Mela IV was being held. An evening presentation was interrupted by the news that the military were in the streets and the government had announced a curfew. The future of the national state is very much in question in both countries.
Tiers ?tat, the term for the commoners of France, has now become the defining expression for the majority of humankind. The Third World is not a name we chose for ourselves. The G8 countries make decisions that have a profound effect on our lives, yet we never chose to be represented by them. So we call ourselves the majority world, for that is indeed who we are, the majority of this world. Our portrayal as icons of poverty is one chosen by the West, through image-makers who are free to roam a world where boundaries exist only for this excluded majority. Europe builds a fortress around itself, choosing carefully whom to include.
Chobi Mela evolved from the need for self-representation of this excluded majority, for the creation of its identity, and for the expression of its creativity. The themes for Chobi Mela have reflected this need. Differences. Exclusion. Resistance. Boundaries. Freedom. These are words that circumscribe our existence. It is through our engagement with what the words represent that we look for our space in a rapidly globalised world.
The selection of Contacts 30 presented a problem. It was clearly one of the key exhibitions in the festival. Isolated in the Bangladesh National Museum, it could be seen in its entirety without casting a shadow on smaller intimate exhibits, which were as important, but with a substantially smaller footprint. The intimacy of one did not impinge on the volume of the other. With that separation removed, could they coexist? Were we in danger of drowning the quieter voices? Would the imposing presence of one, prohibit the quiet reflection necessary for the other? What about the show itself? Would the thirty images presenting thirty years, work in year thirty-two? Given the same images but a changed global dynamic, would the same images have been chosen? One never knows, and perhaps it doesn?t matter. What is being shown is a display in a certain time and space and it is only within that time/ space matrix that it can be negotiated. Festivals are live, as exhibitions are. The historical context of an earlier showing, planned in the same venue and by the same curator, having been removed in protest against censorship, adds a layer of complexity that might escape the viewer, but adds to the legacy of the festival and its history of resistance.
Kwaito Culture
Photographs: Neo Ntsoma
Neo Ntsoma cried at the Goethe Institut Auditorium as she spoke of her isolation in Apartheid South Africa. But they were strong tears. Neo?s personal struggle as a black woman in a white male space, allowed her to look for the changing culture in today?s black South Africa. Her personal project on the SA Youth ID-Kwaito Culture speaks of much more than just the changes within the youth of her nation. The lions have found their storyteller. Ntsoma is a complex person. Highly strung, energetic, intense, passionate, laughing, crying, running, leaping, she is in the middle of everything and everywhere. A spring ready to uncoil. She is also deceptively perceptive. Having faced racism in every guise, she has toughened herself to face life?s challenges. But it is her black identity that has emerged as the soul within her work. She rejoices in her color and rejoices in color. Her search for identity within the black South African youth scene is no nostalgic trip down memory lane, but rather a buoyant leap at the crest of the wave of youth which captures the energy, the dynamism and the joy of a youth determined to find its own expression. Not surprisingly, it is the raw energy of her work that attracts.
The Tigers
Photographs: Gajaani

They call her a terrorist. Gajaani?s work has been rejected by many, as she is a fighter in the LTTE, a listed terrorist organization. The label has of course been given to the ANC, and hence Nelson Mandela, while many who continue to terrorize the world, do so with abandon, knowing there will be no labels to tarnish their image. The labels do not concern me, and while I was intrigued by her history, it was the images I saw that provided the excitement. Never before had I seen the every day lives of the LTTE. Women fighters dancing, combing each other?s hair in the bunkers. Playing musical instruments. The children in bunkers, mines being planted, snipers in camouflage, reminded me it was a war zone I was peering into. For over seventeen years, Gajaani has photographed the war as seen by a Tamil Tiger. I have never met her, and our only contact has been through a mutual friend we both trust. The friend carries our greetings and ferries pictures back and forth. War changes people, but the changes in Gajaani are not simply due to war. She now sees beyond images of war. Her films are lyrical, but also reminiscent of the battle drums of old, strident, passionate and one-sided. She takes still life and sunsets, and photographs abstract shapes in the sand. This is not a photojournalist reporting on a war, but a warrior taking pictures. We may not like it. It might make us uncomfortable. But we cannot deny its existence. This is her war, her life and her call to freedom. In a world dominated by spin and propaganda, I recognize that seeing this work will be disturbing for many. But this is a disturbance that must not be avoided. The work romanticizes a war where many have died, on both sides. Most of them civilians. But to deny this work denies the fundamental inequalities that lead to such wars.
She first showed me her early work. She has sent more work since, along dangerous routes. Films, still photographs, hard images of the devastation of war, gentle images of soldiers being ordinary men and women, children in fear and in play. And she has written letters. I don?t know if Gajaani is her real name. I read again the lines that take on new meaning as the war moves to a more violent chapter. I know she will soon be on the front lines. The photographer will become a warrior again. She will trade her lens for guns.
Dear Shahidul Vanakkam,
…I hope that if our liberation war lets me live then I would love to meet you… Even after an artist?s death, art lives. After death it will be so. I have that small belief…
With love
Gajaani
Modern American Segregationists
Photographs: David Holloway

He hails from a long line of farmers, carpenters, truck drivers, and mechanics. But the storyteller David S. Holloway has gone beyond the farmlands of Oklahoma and forests of Arkansas. The first multiparty elections in Tanzania, the SARS outbreak in Toronto, and the punk rock and politics of Washington D.C. provide the backdrop for the social tensions that his photography explores.
The struggle of working-class Americans give us a window into the realities of a nation so obsessed with world domination that it has forgotten who it is fighting the war for. Race, poverty and violence make their way into Holloway?s lens. His stark black and white images, frightening but beautiful, seduce you with their form before baring their crude baggage. Raw greed, manufactured fear, calculated indifference. Family gatherings fueled by hate.
Contacts 30
Photographs: Contact Press Images

What makes an icon? What does a celebrity fashion photographer choose, to depict the ravages of war? How does a Salgado contact sheet look? The giant contact sheets, reincarnated by the very digital technology that rings its death knoll, reveal the structured approach and the inconsistencies that mark a photojournalist?s quest to find the perfect image. The viewer, like a giant magnifying glass, follows the journey frame by frame. The chosen image separated by curatorial treatment, becomes history. Its neighbors perhaps finding only oblivion. Thirty images. Thirty years. The contacts of the celebrated Contact Press agency span the quintessential moments of the times. Exhibited by curator, president and co-founder Robert Pledge, the contacts span the great moments of history. The death of Chairman Mao Zedong, the fall of the Berlin Wall, the measured tryst between Gorbachev and Reagan, George Bush with his poodle, a distraught Mary Decker photographed by Contact?s other co-founder David Burnett who in a contact sheet of his own, indulges in a self portrait. It makes the complex kaleidoscope that this exhibition mixes and pulls off with gusto.
Nowhere People
Photographs: Swapan Nayak

India is the new darling, and negative stories about the nation refuse to surface. While a caste system refuses to lie down and die, a growing economic disparity amidst growing economic growth, fails to leave an invisible trail. The nation burns. The seven states in the geographically isolated and economically underdeveloped North-East India are home to 200 of the 430 of its tribal groups. With the poor moving to the less poor zones, an influx of migrants from neighboring areas leads to ethnic conflicts over land and fighting for political autonomy or secession.
The numerous political parties and armed groups that have mushroomed resort to ?ethnic cleansing? in order to defend their interests against a real or perceived enemy. ?Divide and Rule? rules. Violence has broken out in the states of Assam, Manipur, Nagaland, Tripura and Arunachal Pradesh, involving at least eight different ethnic groups (Bodos, Nagas, Kukis, Paites, Mizos, Reangs, Bengalis and Chakmas). The largest forced displacement movements have occurred in the states of Assam, Manipur and Tripura.
Swapan Nayak operates within this unpredictability. Spending days on boats that navigate the treacherous waters of the Sunderbans, and mixing with the tribes that want revenge for their displacement, he travels along with his photographs. Together, they take the viewer into an unknown India.
Naxal Women
Photographs: Shahidul Alam; Interviews: Nesar Ahmed; Translations: Rahnuma Ahmed

They had left their village homes to join the class struggle. They were young. Some were, so to speak, ?born? to the party. Communist party members were frequent (albeit clandestine) visitors to their homes, which acted as party ?shelters.? For some, there were no restrictions but for others, it wasn?t easy. Daughters wanting to go into politics, and underground politics at that? Never. Several were severely beaten by their families. The women rebelled. A woman in her early teens, whose marriage was being hurriedly arranged, left home and went to the Party-controlled ?free? zone. One was forced to leave home when the Awami League?s para-military forces, the Rakkhi Bahini dowsed their house with petrol and set fire to it. Party members had been frequent visitors there. It was 1973.
They worked mostly as Political Commissars, doing organizational work. Some took part in armed conflicts. Two were chiefly couriers, one also cooked for Party members. Most married Party comrades. The Party vetted friendships. Conditions were attached: a year?s separation, no letters, monitored visits. Weddings were simple affairs, a few comrades present, signing on a piece of paper, which belonged to the Party. A handshake, an exchange of garlands. Perhaps a meal. But some weddings?maybe that of a party leader?were extravagant.
State repression continued. Cooption also occurred. In late 1979, the Party disavowed armed struggle. Its policy of annihilating class enemies had meant… ?we created enemies in our own villages.? Women comrades were asked to return to their families, or to marry and settle down. Some feel there was no other option since the party was organizationally shattered, with many of its members either dead, or imprisoned.
It?s an open question. These women?s? recollections help flesh out the actual lives and concerns of Bangladeshi Naxal women, women who are largely absent from Party literature and male-centered traditions of history-writing. A tradition that I have tried to challenge.
Tears Cloud Peace
Photographs: Masaru Goto

Even in the paradise on earth, there is a line of control. Bullets kill, shrapnel maims. People ?disappear.? Forever. Mothers mourn children?s death. Lovers part. 80,000 dead. Men, women and children from both sides. The 440 kilometer line of control. Masaru Goto works on the Michael village of border district Kupwara. A few miles from this line of death. The line of control becomes the line of fire. They are engulfed in flames. They die from each other?s bullets. Indians. Pakistanis. Kashmiris. In death they finally unite. Away from the romantic Shikara rides, the Shalimar Gardens, the snowcapped mountains. Away from the polarized depictions of freedom fighters/terrorists. Away from the militancy and the occupation. Goto shows us the lives of ordinary people not searching for paradise, but seeking survival on earth.
Not Your New York
Photograph: Pablo Garber

Digital postcards in a digital age. Fleeting snapshots of Pablo Garber?s images. He gingerly places his feet on a moving, shifting, amorphous earth. Unsure of his presence. Indignant in his reasoning for making pictures, Garber is a stranger in a city he longs to call his own. The exuberance of a city that is larger than life. Here fortunes are made. Careers launched. But Garber rejoices in serendipity. He soaks in the larger than life city that is the Big Apple, rejoicing in its excesses, chuckling at its follies. He remembers the city streets as he had last walked them, nearly twenty years ago. He recognizes the shadow of 9/11.
He hears the city weeping as he looks for the missing World Trade Center. Garber?s work has always dealt with relationships. In the streets he searches for his own relationship with a long lost city.
A River Has Two Sides
Photographs: Jerome Ming

The photographs by Jerome Ming are rarely ?decisive moments.? Rather they reflect the seemingly timeless character of people?s struggle to survive. What is decisive, are the circumstances, often beyond their control, that shape their lives. As many other concerned photographers have done, Ming documents the plight of disenfranchised communities, but in doing so he neither sensationalizes their presence, nor disengages them from the evolving cultural shifts that have become a permanent characteristic of people in transition. They are subdued photographs that seep into you, rather than images that scream for attention. They are photographs that beg reflection, which rarely scream, but are always there. Echoing in some ways the inevitability of the changes and the relentless march of ?progress? as defined by others.
The War Rooms
Photographs: Tarek Al-Ghussein and Chris Kienke

It is an unusual mix. Tarek Al-Ghussein and Chris Kienke. A Palestinian and an American. But it is a war that belongs to us all. In a globalized world, the invasion of Iraq affects all our lives. The images, seemingly arranged at random, become the pixels of war. Choosing not to choose, they let a mechanical selection determine the sequence. Yet another dehumanization in this ?clinical? war game. Like the old telex machines churning out ticker tape, these mobile images converted to still life are like corpses of movies. Segments of life frozen by war. Pop stars, sports fields, cartoons, most view programs on spin, smart bombs homing in on target. Yet there is no cynicism depicted in this collage. The cynicism is implied. Saddam, Nighthawks, Bush and his poodle, all serve to create a relationship with the viewer, which is both complex and riveting. Are we awed, enraged, disillusioned, relieved? None of these. In this image-saturated world of ours, we have become desensitized to the messages. Engulfed in a war room, we whisper. Careful not to annoy the generals. Displaced from its roots, this festival within a biennial-festival, tries to recreate a sense of place, a sense of community and a sense of struggle. The passions that gave rise to Chobi Mela, the need for such a festival, the photographic family that has grown around it, has a collective identity that will not be diluted in a bigger event. It draws on the inherent story exhibiting qualities to which the photography lends itself. While the work shown encompasses the globe, the photographers address issues that are universal in themselves, regardless of their geography.
Shahidul Alam
Brussels 19th October 2008
Festival dates: 19th October 2008 – 4th January 2009
Special thanks to: Nesar Ahmed, Rahnuma Ahmed, Abdullah Al-Faruque, Refanur Akhtar Moli, Md. Shafiul Azam Khan Tushar, Dominique Deschavanne, Mohammed Harun Ur Rashid Nipun, Irfanul Islam and Tanvir Murad.




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.