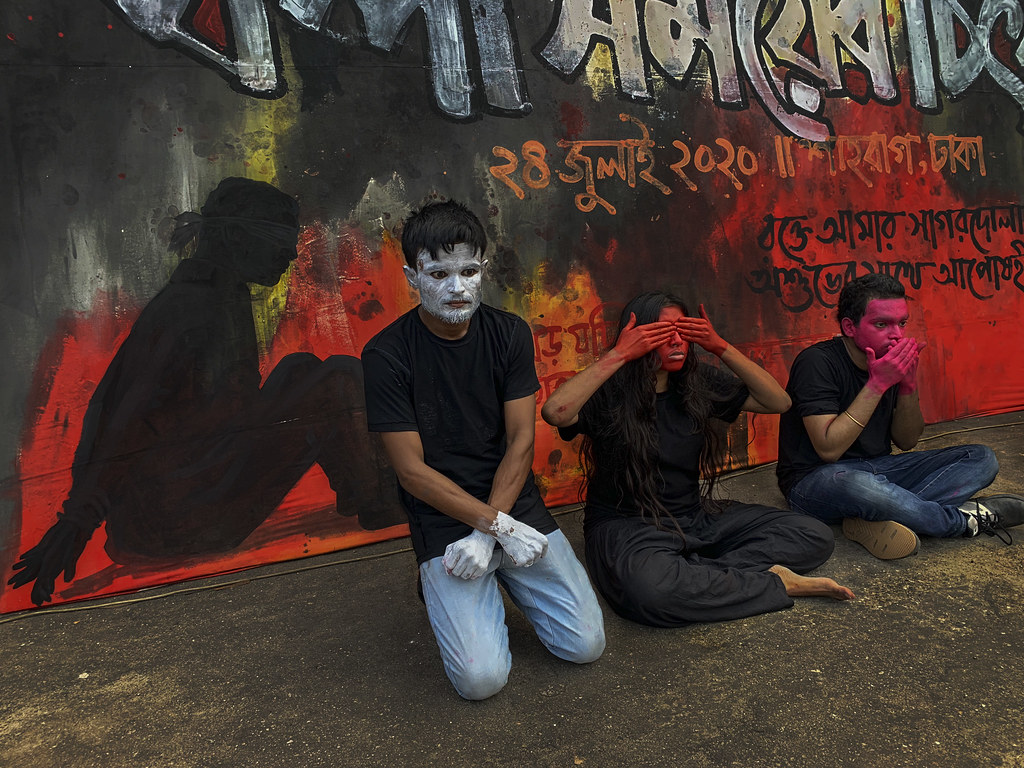rahnuma ahmed
I have not acquired any fortune but I have my paternal estate and the pension of a Subedar. This is enough for me. The people in my village seem to respect me, and are now fully satisfied with the ease and benefits they enjoy under British rule.
Thus wrote Sita Ram in From Sepoy to Subedar, first published in 1873, sixteen years after the first war of independence (the British still refer to it as the Indian Rebellion, or the Indian Mutiny).
Sita Ram wrote the manuscript at the bidding of his commanding officer Lieutenant-Colonel Norgate in 1861, his son passed it on to the Englishman; the manuscript is supposed to have been written in Awadhi, Norgate translated it into English. An Urdu translation is also heard to have surfaced the same year. Few copies are known to have been sold, until 1911 that is, when a Colonel Phillott created a new syllabus for Hindustani exams, taken by colonial officers to test their knowledge of the language. Phillott himself translated the book into Urdu, and from then onwards, the autobiography of Sita Ram, who worked in the Bengal Native Army of the East India Company for forty-eight years (1812 to 1860)—became a ‘key text’ for British officers. The book was still part of the curriculum in the 1940s, it was translated into Devanagari in the same decade; a new and illustrated edition of the book (Norgate’s English translation), was brought out by James Lunt, as late as 1970. Continue reading “Propaganda, and the suppression of dissent”