Nahida Ashrafi. Photo: Rahnuma Ahmed
Tag: trade
The Price of Social Distancing
Rahnuma forwarded me Laily’s wrenching FaceBook post. Her father is dying, far away in a UK hospital. Heart breaking, holding back tears, she and her family watch from afar. Unable to touch, to hold, to caress the person who is dearest to them. This is what Corona means in real terms. It was through her research on one of my heroes, the peasant leader Abdul Hamid Khan Bhashani, and later through them staying at the Pathshala Guest House, that we got to know her. Bhashani’s principle of putting nation before self and his simple lifestyle is a very distant reality from the ruling politicians of today. Despite its pain, Laily’s post reminded me of my own dad and my childhood. I remembered dad resting in his easy chair. His belly just the right slope for us kids to use as a living slide. We used to call him bhalluk (bear), and every day as he rested after lunch, my cousins and I would line up behind the easy chair, clamber up to his shoulders and slide down his belly. Mum would freak out, as my dad had osteomyelitis as a child and had never fully recovered. His shins were always exposed and very fragile. Quite apart from wanting him to rest, the idea that we might aggravate his injury worried her. Abba was unperturbed, happy to be teddy bear to a room full of kids. We’d run back to the end of the queue to slide down again. We were always tired before Abba ever did. We didn’t think of it as physical contact in those days. When Abba died, I remember feeling the stubble that had grown on his soft skin, as I stroked him before we laid him down.
Newcomers to Bangladesh are overwhelmed by the generosity of our village folk. They love it when strangers clasp their hands, but are somewhat unsure when seconds, sometimes minutes pass, before their hands are reluctantly released. Years ago, when we at Drik were trying to improve our English skills, we struck a deal with the local office of the British Council. Unable to pay for the expensive English classes, we negotiated a barter. We would do their photography. They in turn, would teach us English. It wasn’t just language skills though, it was learning English culture. One of the first things our English teachers told us was to release the hand quickly! Prolonged physical contact could make the English squirm.

The Best Years of My Life

Press release
German Foreign Office and Neue Galerie Berlin will present Shahidul Alam at Deutsche Welle?s Global Media Forum and at the Global Forum on Migration and Development in Berlin.
With the book publication and the exhibition ?The best years of my life. Bangladeshi Migrants in Malaysia? the international well-known photographer and activist Shahidul Alam will be present on Monday, June 19, 2017 through the Neue Galerie Berlin and with the support of the German Foreign Office on the Global Media Forum of the Deutsche Welle. After the end of the forum in Bonn, the exhibition will be on display at the German Foreign Office in Berlin from Thursday, June 23, 2017, and will be part of the Global Forum on Migration and Development from 28 to 30 June. The Finissage will be published on 30 June 2017 at the Federal Foreign Office with a greeting from the State Secretary Dr. Markus Ederer within the framework of the GFMD. The artist will be present in Bonn and Berlin and will be available for questions and interviews. Further information on the exhibition and the artist in the appendix.
As an additional digital component, the Neue Galerie Berlin, together with the technology partner snap2live, presents the newly developed image recognition app ?Neue Galerie Berlin?. All pictures of the Alam exhibition can be scanned with the app (tentatively available on Android). Behind the pictures
About
In 2016 Tanja von Unger founded the Neue Galerie Berlin (www.neuegalerieberlin.de).
To provide a relevant platform beyond photography the businessmodel
also collaborates with publishing groups and institutions and is known for its groundbreaking presentation of photographers and their works at economic conferences and events such as the Economic Summit of the Su?ddeutsche Zeitung, Falling Walls Conference, Rheingauer Economic Forum, Global Solutions G 20 Conference of the Dieter von Holtzbrinck publishers.
Snap2Life create apps for companies in the media, publishing, automotive, business, sports and advertising sectors. Most of these apps are equipped with our innovative image recognition functionality, which we also provide as an API for integration into other apps. In a fraction of seconds we connect the offline world with any kind of relevant content from the online world.
The Deutsche Welle Global Media Forum (GMF) is the Place Made for Minds, where decision makers and influencers from all over the world come together. It?s the global platform put on by Deutsche Welle and its partners and the place where you can connect and strengthen relations with over 2,000 inspiring representatives from the fields of journalism, digital media, politics, culture, business, development, academia and civil society. The conference provides a unique opportunity to network, get inspired and collaborate using a wide variety of state-of-the-art formats.
http://www.dw.com/en/global-media-forum/global-media-forum/s-101219
?Towards a Global Social Contract on Migration and Development?
Tenth Global Forum on Migration and Development Summit 28 to 30 June 2017, Berlin
Germany and Morocco have assumed the co-chairmanship of the Global Forum on Migration and Development (GFMD) from 1 January 2017 until 31 December 2018. During this two-year period, the focus will be on the contribution of the GFMD to the United Nations? Global Compact on Migration. The Compact is intended to constitute a strong signal of the international community for an enhanced global migration policy, to be adopted by the community of states in 2018.
https://gfmd.org
Modi visits Bangladesh, but Teesta is not even in the agenda
by Taj Hashmi
Last time I met my old friend Gowher Rizvi at his office in December 2011, he was very upbeat and optimistic about the ?impending? Teesta water sharing agreement with India. He seemed to have reposed absolute trust in what Manmohan Singh ? a fellow Oxford alumnus ? had promised him in this regard. Although I was still a bit skeptic about the deal, I brushed aside my skepticism momentarily, thinking the Oxford Old Boy camaraderie might have worked to the advantage of Bangladesh.

New humility for the hegemon
Subscribe to ShahidulNews
India and its near-abroad
Too slowly, India is realising that poor relations with its South Asian neighbours hold back its global ambitions
Jul 30th 2011 | from the print edition of the Economist

NO ONE loves a huge neighbour. For all that, India?s relations with the countries that ring it are abysmal. Of the eight with which it shares a land or maritime boundary, only two can be said to be happy with India: tiny Maldives, where India has the only foreign embassy and dispenses much largesse, and Bhutan, which has a policy of being happy about everything. Among its other South Asian neighbours, the world?s biggest democracy is incredible mainly because of its amazing ability to generate wariness and resentment.
Until recently it operated a shoot-to-kill policy towards migrant workers and cattle rustlers along its long border with Bangladesh. Over the years it has meddled madly in Nepal?s internal affairs. In Myanmar India snuggles up to the country?s thuggish dictators, leaving the beleaguered opposition to wonder what happened to India?s championing of democracy. Relations with Sri Lanka are conflicted. It treats China with more respect, but feuds with it about its border.
As for Pakistan, relations are defined by their animosity. One former Indian diplomat likened reconciling the two nuclear-tipped powers to treating two patients whose only disease is an allergy to each other. The observation underscores the fact that it takes two to have bad relations, and to be fair to India plenty of problems press in on it?many of them with their roots in India?s bloody partition in 1947. Pakistan has used a long-running territorial dispute over Kashmir as a reason to launch wars. It also exports terrorism to India, sometimes with the connivance of parts of the Pakistani state. India thinks Bangladesh also harbours India-hating terrorists.
With the notable exception of India?s prime minister, Manmohan Singh, who has heroically persisted in dialogue with Pakistan in the face of provocations and domestic resistance, India?s dealings with its neighbours are mostly driven by arrogance and neglect. It has shared shockingly little of its economic dynamism and new-found prosperity with those around it. Just 5% of South Asia?s trade is within the region.

Too little and too late, the neglect is starting to be replaced by engagement (see?article). This week Sonia Gandhi, dynastic leader of India?s ruling Congress Party, visited Bangladesh?a first. And on July 27th India?s foreign minister hosted his Pakistani counterpart, the first such meeting in a year. He promised a ?comprehensive, serious and sustained? dialogue.
A new regional engagement is prodded by two things. China?s rapid and increasingly assertive rise challenges India?s own regional dominance. As a foundation for its rise, China pursued a vigorous ?smile diplomacy? towards its neighbours that stands in contrast to slothful Indian energies. The smile has sometimes turned to snarl of late (see?Banyan). Even so, China?s engagement with its neighbours has allowed it both to prosper and to spread influence.
 interactive map displays the various territorial claims of India, Pakistan and China from each country’s perspective
interactive map displays the various territorial claims of India, Pakistan and China from each country’s perspectiveSecond, dynamic India can hardly soar globally while mired in its own backyard. Promoting regional prosperity is surely the best way to persuade neighbours that its own rise is more of an opportunity than a threat. Yet India lacks any kind of vision. A region-wide energy market using northern neighbours? hydropower would transform South Asian economies. Vision, too, could go a long way to restoring ties that history has cut asunder, such as those between Karachi and Mumbai, once sister commercial cities but now as good as on different planets; and Kolkata and its huge former hinterland in Bangladesh. Without development and deeper integration, other resentments will be hard to soothe. It falls on the huge unloved neighbour to make the running.
BBC Documentary on Sino-Indian Rivalry and Bangladesh
http://downloads.bbc.co.uk/podcasts/worldservice/docarchive/docarchive_20100630-1227a.mp3
Connectivity: The India-Bangladesh land bridge
Subscribe to ShahidulNews
Himal Magazine
February?2011
By?Kanak Mani Dixit
Can a formal bilateral communiqu? be a ?game changer?, foretell a ?paradigm shift?, in a Southasian relationship? If India and Bangladesh manage to follow through on promises to open up their economies for transit and trade as set out in a memorandum of January 2010, a new era could dawn across the land borders of Southasia. The challenges are bureaucratic inertia in New Delhi and ultra-nationalist politics in Dhaka.
The political partition of the Subcontinent in 1947 did not have to lead to economic partition, but that is ultimately what happened. This did not take place right away, and many had believed that the borders of India and Pakistan?s eastern and western flanks were demarcations that would allow for the movement of people and commerce. It was as late as the India-Pakistan war of 1965 that the veins and capillaries of trade were strangulated. In the east, in what was to become Bangladesh just a few years later, the river ferries and barges that connected Kolkata with the deltaic region, and as far up as Assam, were terminated. The metre-gauge railway lines now stopped at the frontier, and through-traffic of buses and trucks came to a halt. The latest act of separation was for India to put up an elaborate barbed-wire fence along much of the 4000 km border, a project that is nearly complete. Today, what mainly passes under these wires are Bangladeshi migrants seeking survival in the faraway metropolises of India ? and contraband.
 |
| Photo credit: Sworup Nhasiju |
Continue reading “Connectivity: The India-Bangladesh land bridge”
WikiLeaks cables: Bangladesh Gas
Subscribe to ShahidulNews
US nudged Bangladesh to allocate gas blocks
BS Reporter / New Delhi December 25, 2010, 0:15 IST
Every time India would ask Bangladesh for rights to explore gas, Dhaka would say the country had to first find if there was gas available at offshore locations. For the last one year, the issue hasn?t even been mentioned in discussions with Bangladesh, top petroleum ministry officials said. But India?s loss has been the US gain and it managed to walk away with the prize.
WikiLeaks tapes released late last night revealed how US-based ConocoPhillips was selected from a field of seven bidders and awarded two offshore blocks for exploring gas in 2009. The company was awarded a production sharing contract, with a provision to export the gas in the form of liquefied natural gas in the untapped areas of the Bay of Bengal. The bidders had agreed to stay away from disputed waters in the Bay of Bengal, something US Ambassador to Bangladesh, James Moriarty mentioned in his cables sent in July 2009. Conoco got the contract in October 2009.
Moriarty met Bangladesh Prime Minister Hasina Wajed?s energy adviser, Tawfiq Elahi Chowdhury, and got him to assure that ConocoPhillips would be awarded two of the uncontested blocks and Chevron given permission to go ahead with the first of the three compressors necessary to improve flow in Bangladesh?s main gas pipeline. Within three months, the Bangladesh government complied.
Defending themselves against the charge that they had allowed the US to have an advantage by not being proactive themselves, Indian Petroleum Ministry officials said Indian finds of gas had reduced the pressure to secure gas from Bangladesh.
WikiLeaks tapes also revealed that Moriarty urged Chowdhury to approve plans by British company Global Coal Management (GCM) to begin open-cast coal mining in the country?s Phulbari area. In the cable, Moriarty quoted Chowdhury saying the coal mine was ?politically sensitive in the light of the impoverished, historically oppressed tribal community residing on the land?.
The energy advisor, however, agreed to build support for the project through the parliamentary process, Moriarty said in the cable.
In a cable posted by WikiLeaks that was sent in July last year, Moriarty said he had urged Chowdhury to authorise coal mining, adding ?open-pit mining seemed the best way forward?. Later on in the cable, Moriarty said, ?Asia Energy, the company behind the Phulbari project, has 60 per cent US investment. Asia Energy officials told the ambassador they were cautiously optimistic that the project would win government approval in the coming months.?
The ?Phulbari killings? as they are known took the lives of three boys in 2006 when police fired at a demonstration near the mine site. Asia Energy?s shares had crashed in the international market as a result and the company had to undergo a brand change, including a name changing.
In the WikiLeaks cables, Moriarty?s conversations with Indian ambassador Pinaki Ranjan Chakravatry, by contrast, revealed no discussions of a commercial nature, only a general approval by India of the change in government in Bangladesh and US endorsement of a joint South Asian task force on counterterrorism.
India?s high commissioner in Dhaka obligingly told the US ambassador that while India would ?prefer a primarily bilateral engagement?, Bangladesh might want a regional force for political reasons ? allegations that she was too close to India.
Chakravarty spoke of Bangladesh?s keenness to ?invest heavily in Bangladesh?s moribund railway system? including reconnecting the Bangladeshi railroad system to Agartala in Tripura. He said Indian companies would be interested in setting up power plants in Bangladesh, though the price of electricity ?is still under negotiation?. The US takeaway from the conversation is that regional counter-terrorism cooperation would help US assets enormously. Much of the rest is yet to become a reality
River and Life
Subscribe to ShahidulNews
![]()
They meander and glide. They unfurl with the rage of monsoon fury. Quietly they flow in the misty winter morn. Rivers thread the fabric of our land. Embroider patches of fertile delta. They are the nakshi kantha of our rural folklore. Life giver, destroyer, enchanter, they have inspired the greatest myths, formed the tapestry for the most endearing love songs. Our Bhatiali has been shaped by the lilt of the boatman?s lyrics drifting across the waves.

It is this fluid, amorphous, ephemeral and elusive visual that Kabir tries to hold in his rectangular frame. It is a frame heavy with the burden of its task. The rivers that float like a gossamer across the green delta hold untold stories. Tales of strife and endurance. Of the fullness of life. Of abundance ebbed, and anger unleashed.

Kabir finds the rapidly disappearing sailboat drifting in the late afternoon light. The extinction of this species owes not to the depletion of its habitat, or to the oft-blamed climate change, but the advent of technology. Oil guzzling, deep tube well engines have unseated the wind from its traditional role.? A lone sail, bright red and taut against a blue sky defiantly throws a gauntlet to the mechanized usurper.

Swirling swathes of jute cleanse themselves in the very water that nurtured them in their youth. Wispy traces of boatmen recede into the darkness of dusk. The cool blue light of the evening sky wraps itself round a homebound farmer. Barefoot women, walk home after a day?s work, like a string of pearls along the sandy shores of a receding river. Parched river beds, like a desert amidst the oasis, make horizon-less paths for weary travelers to tread.

Fishermen, silhouetted against a brooding sky, cast their nets more in hope than in expectation. Overfishing of uncared for rivers, bloated with toxic waste, yield little to those who have made the river their home. Indeed it is their ancestral home. A liquid home that knew no government deeds, and obeyed no official maps. But the rules have changed. City folk whose feet walk only on the cool marble of urban dwellings own fishing rights to rivers they may never have seen. The fishermen who were raised in these waters are now outlawed in their own turf.

Still the river gives. Joy and thrill to the racing crews that steer swiftly through the monsoon breeze. Respite to the sun baked skin of naked boys, sari clad maidens and heavy hoofed buffalos. Turgidity to the parched leaves of the newly planted grains of rice. Looming clouds in azure skies to the poet who longs for whispering words. Winding arcs of sinewy lines to the painter?s canvas in search of form.

The great rivers, once bountiful and brimming, have formed the supple spine of our deltaic plains. Choking in silt, poisoned by waste, waterways throttled by land grabbing encroachers, the lifeblood of our deltaic plains weep dry tears as their once glistening bodies writhe in pain. It is a pain city dwellers are deaf to. A pain that short sighted politicians and profit seeking urban planners have no time for. Kabir rejoices in the vigour of the river. Is saddened by its pain. His portrait of the river shows both its wrinkles and its smile.

Photographs: Kabir Hossain
Text: Shahidul Alam
The exhibition “River and Life” by Kabir Hossain will remain open until the 17th July at the Drik Gallery II from 3:00 pm till 8:00 pm
Give photography a chance
By Giedre Steikunaite

A photograph?s story is not only the one told in the image. Who took a picture, and why, also matters. Now who takes pictures of the developing world, and why?
?The vast majority of the published images that we see of the developing world are taken by predominantly white, predominantly male photographers from the ?north? or the ?west? (whichever language you use) and we think a) that this is unfair and b) that it leads to a distorted view lacking balance. The distorted view is intrinsically dangerous as it perpetuates stereotypes,? said Dr Colin Hastings, responsible for strategy and financing at?Majority World, in an interview with?igenius.
How about giving Majority World photographers a chance to represent the world they live in themselves?
Majority World, a global initiative set up to provide a platform for indigenous photographers from the Majority World to gain fair access to global image markets, is in its third year. Their?online library contains loads of photographs, both individual and featured, ranging from Adolphus Opara?s?Slum Aspirations to Aaron Sosa?s?Daily Havana to Saikat Ranjan Bhadra?s?Grey Reality. The idea is to shift the current practice of the global North photographing the global South and allowing the South to do it itself.
Photographers in the developing countries face numerous challenges. At first it was said that they don?t exist, then that they ?don?t have the eye?. But apart from these prejudices, there are serious problems photographers have to deal with: lack of access to the internet, costly cameras, scanners, and computers, lack of awareness of Northern markets, no money to travel and build up a portfolio, poor business and marketing skills and, probably worst of all, untrusting potential clients, who are nervous to assign an unknown photographer in a distant land.

Let?s come back to those white males who dominate the global photography market with their orthodox reflections of the Majority World. And aid. ?Development isn?t simply about money. What about developing mutual respect; enabling equitable partnerships; providing enabling environments for intellectual exchange? What about creating awareness of the underlying causes of poverty? These are all integral parts of the development process. When all things are added up, cheap images providing clich?d messages do more harm than good. They do not address the crucial issue: poverty is almost always a product of exploitation, at local, regional and international levels. If poverty is simply addressed in terms of what people lack in monetary terms, then the more important issues of exploitation are sidelined,? wrote Shahidul Alam, an international photojournalist and Chairman of?Majority World in?The New Internationalist in 2007.
Back then, the situation started to change, if only very slowly. In that same article, Mr Alam agreed that due to the media?s deteriorating financial situation, some adjustments had taken place: with media?s budgets squeezed, it?s getting harder to fly Western photographers to make some shots in a far away land.
This is where local photographers come in handy, but the fact is yet to be recognized by news outlets. And it ain?t so sunny out there, either. ?Certain rules still apply of course, such as the vast differentials in pay between local and Western photographers,? wrote Mr Alam.
I asked Dr Colin Hastings who works tirelessly to promote Majority World photography, how to encourage global media organizations to use images made by local photographers. He said we need to make a distinction between purchasing images pre-taken and uploaded into an existing photo library (known as ?stock photography?) and ?assignments?, where a photographer is commissioned to take specified types of image for a particular purpose.
?As for stock images, all we ask is that Majority World photographers have equal opportunities to get their images into photo libraries and showcased across the world and available for sale. At present they are marginalized and face many disadvantages. It is providing an equal playing field that is at the heart of what Majority World is about, enabling them to have the resources that Western photographers just take for granted.
?When it comes to assignments, Western media, editors and photographers tend to go out with a predetermined agenda often to find images to confirm their existing preconceptions and stereotypes often based on information that is way out of date. This is an issue of editorial bias, i.e. do you really want to find out the truth (whatever that is).
?Well, you are more likely to find out from someone who is of the culture, speaks the language, understand the nuances and the history, than from someone who jets in for a few days, is essentially a voyeur from the outside of the culture, and may be viewed with a mixture of incredulity and suspicion by those being photographed… To say nothing of the ethical issues about whether anyone ?should? be or has the right to take photos in any situation.
?It is right to acknowledge that it is not a simple matter to employ and brief an unknown photographer at a distance, especially where there are language and other cultural barriers to communication. But that can also be too easily used as an excuse. There are suitable and reliable photographers out there who do fine work. Part of our role is to take the risk out of this process by finding the most suitable photographer and acting as a communications facilitator.
?We have to help the client to change their behavior and ways of doing things and also help the photographer to understand and to respond to the clients? needs.? It?s complex!?
Three years ago, Dr Hastings expressed his wish for every postcard sold in a tourist destination in the global South to be taken by a local photographer. ?My vision is to see a whole range of beautiful high quality photographic products – cards, calendars, diaries or digital products images – taken entirely by Majority World photographers,? he said.
We?re not there yet, but hopefully on the way.
Photos: fish by?Partha Sarathi Sahana, water by?prakhar
The Price for "Progress"
Subscribe to ShahidulNews
http://www.newint.org/issue372/exposure.htm
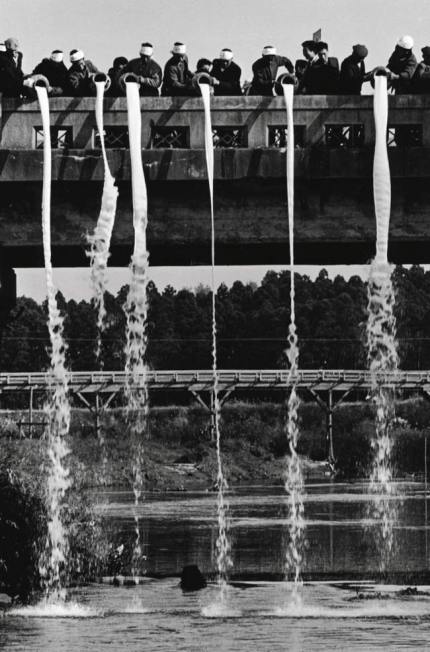

Shinzo Hanabusa is yet another artist to be featured in the upcoming festival of photography, Chobi Mela III. Hanabusa’s work on Japanese farmers provides a fascinating insight into the cost of ‘progress’, in a nation like Japan.
The Second World War had adversely affected farming in Japan. I began producing a documentary on farming in 1962. The farmers were not getting a fair price for their milk. Then Japan started importing powder milk and things got really bad. In 1966 I heard rumours that the farmers in Akita were setting up a resistance movement. Following newspaper leads I went over to the locality. I was very upset, when I saw them throw the milk from the bridge as a sign of protest, at the fact that they had been reduced to this. But a big publication, Ewanami Shoten, printed the photograph and it helped turn things around a bit, so I felt good afterwards. I have since become known as ‘The Milk Photographer’. I hope the publication of this photograph in Southern Exposure helps farmers around the world get a fair price for their produce.
Shinzo Hanabusa, Japan