Subscribe to ShahidulNews

rahnuma ahmed
Last year, in June, she had left Dhaka and her pet dogs to take up her new assignment in Baghdad. Patricia Butenis has returned, this time on a private visit, to fetch her dogs, and to visit her old workplace.?Amader Shomoy, March 3, 2008??
Political speculation was rife. Was she on a special assignment? Was her visit timed to coincide with the ex-president of Pakistan Wasim Sajjad?s visit to Dhaka? Had Sajjad gone to Geeta Pasi?s home, the US charge d?affaires, where Butenis was staying, to meet with the latter? After all, Butenis had earlier been posted in Pakistan. Was she here to hold meetings with the opposition party leaders of Bangladesh? Or was it secret meetings with top military and civilian officials?
Not many newspapers had reported the pet dog story. US embassy sources had stressed that it was strictly a private visit, that she was not here on any special assignment, that her itinerary had not been made public out of security considerations. That she would return directly to Baghdad.
I read and re-read the newspaper reports. Butenis, it seems, had attended both private and official programmes. She had gone to a dinner given in her honour by the Canadian high commissioner. She had gone to a US embassy organised lunch at Dhaka?s Westin hotel. She had gone to the UNDP-organised ?Celebrating the Halfway Mark of Voter Registration? programme, attended by top Election Commission officials, senior-most military and civilian officers, political party leaders, heads of diplomatic corps, and foreign diplomats. I read the newspaper reports carefully. Renata Dessallien, the UNDP resident representative, had profusely thanked both the Election Commission and the army for the progress made. Bangladesh, she had said, was on its way to rescuing democracy, to putting it back on track. The UNDP would advise other countries to follow Bangladesh?s example, to make a similar ?golden voter list,? complete with voter photographs and national ID cards. Interesting. I returned to tracking Butenis, and found that she had also attended a meeting with US embassy officials in Dhaka. She had spoken of her seven-month-long experiences as the deputy chief of the Baghdad mission.?
But it was the pet dog story that intrigued me. I carefully went through some more newspapers. According to a high-up government source, before leaving Dhaka middle of last year Butenis had said she was leaving her ?pet dogs? behind. She would return to fetch them after she had settled down in Baghdad. Could this be the reason for her visit??The reporter didn?t seem convinced?(Shamokal, March 2, 2008).??
It seemed trivial, but I was piqued. One dog? Or two? Some reports had said ekta kukur (Jaijaidin, March 3, 2008). Others did not mention numbers. They used kukur, which is a collective noun. It could well mean several. A couple of other reports, these were later ones, made specific mention of two, duti posha kukur (Amader Shomoy,?Jaijaidin).???
Were they she-dogs? Or, he-dogs? Maybe one of each? I remembered Butenis had been a strong advocate of gender equality. I remembered the introductory words of her 2007 International Women?s Day speech, ?As we celebrate International Women?s Day this month, I hope everyone will take the time to recognise that women are uniquely valuable and productive members of our society?? I remembered her condemnation of economic discrimination against women, her stand against women?s trafficking, against domestic violence. But then I thought, surely this was stretching it too far? One may well be pro-women, but does that necessarily mean, one of each, in selecting pet dogs? And of course, pet-lovers have to take other things into account (whether they want their pets to have puppies, or get them neutered, a whole load of things).???
I was also worried over my choice of words. The female of the canine species? Terribly outdated. She-dogs? Clumsy. And then I remembered, the word ?bitch? is thought to be less offensive nowadays. I remembered that earlier meanings of malicious, spiteful, domineering have given way to feminist attempts to appropriate the word. Such as?Bitch magazine?(1996), billed as a feminist response to pop culture. I remembered third wave feminist attempts to inscribe new meanings. Bitch, as in women who are strong-minded. Assertive. In total control.??
But I speak of she-dogs. Not women.
Loving dogs
?
I grew up watching Lassie, an American TV serial in the mid- to late-sixties. Lassie, a Yorkshire collie, had seemed incredibly beautiful. Very dignified. Almost human.
It was later, much later that I tried to develop a critical appreciation of modern pet-hood as a western cultural phenomenon. As a kinship phenomenon. I thought of what Marc Shell, an anthropologist, had said. Pets in the west give their owners, ?pleasure, companionship, and protection, or the feeling of being secure.? Shell was writing of the mid-1980s. But was it always like this in western culture? From time immemorial??Jenkins?says, no. Lassie, says Jenkins, was a creation of 19th-century bourgeois imagination, of those who viewed the onset of modernity with a sense of nostalgic loss. As old social commitments gave way to ?alienated and individualistic urban life,? a dog became a ?man?s best friend.? Eric Knight?s Lassie, says Jenkins, stands at the nexus of two new ideas. Children, no longer sources of productive labour, are re-imagined as sacred and innocent. As repositories of parental affection. Dogs are also re-imagined. They are no longer domesticated animals valued for their productive labour, or their exchange prices. They are transformed into pets. Into repositories of sentimental value.?
I am still curious. Of course, I have nothing against pets, I have nothing against dogs, but I fee
l there is more to know. What about today, the 21st century? The love for pets, for dogs seems to have grown more intense, deeper. I want to know what western scholars, those who examine their own social and cultural practices, think. I want to know how intense love and murderous rage can coexist in the modern subject.?
I come across an article by?Heidi Nast, a critical animal geographer. Nast speaks of the here-and-now. She says pet animals have emerged in the 1980s, and more so in the 1990s, as ?highly commodified and valued objects of affection and love.? This, she says, coincides with the rise of post-industrial spaces, and with intense consumption, in the US, and other western countries (spreading outside the west too, in Hong Kong, China, Mexico, South Korea). She writes, the allure of pet animals resides in part ?because they can be anything and anyone you want them to be.? Pets, specially dogs, supersede children as ?ideal love objects.? They are more easily mobilised, need less investment, and to quite an extent, can be shaped into whatever you want it to be, a best friend, an occasional companion. Nast speaks of new shared-experience activities that bond pets and their owners (some prefer the word ?guardians?): dog yoga (or doga), which started in the US, in 2001. And, formal dancing with dogs, this began in Canada and England in the late 1980s. Nast agrees that pet-animal ownership is not radically new. That elites have pampered pet-animals for millennia. But, what is new is the degree of financial, emotional and cultural investment in pet-animals, its geographical scale, and the level of intensity. Things unheard of even twenty years ago.???
Reading Nast I learn that popular support for a national ?No-Kill? movement in US pet shelters emerged in the 1990s (where four million animals are annually killed). That the movement aims to stop euthanising adoptable dogs and cats, by spaying and neutering animal-pets, and working towards greater pet health and adoption rates. I learn that these social tendencies have led to a much greater popular interest in animal rights, a much broader popular participation in animal rights activities. And that this broadened interest has used the rights of animals to treat cultural groups with different sensibilities about the animal world, as the ?other.? Nast reminds us of Bridget Bardot, ex-actress, later a celebrity animal rights activist, who had spoken hatefully of the savagery of Muslims. Because of their slaughtering practices. All in the name of animal rights.???
Nast does not think that the affection-love with which pet-animals are treated is unproblematic. She thinks that the ?escalation in human cruelty to, and dominance over, humans? that the 21st century is witnessing is not un-connected to intense pet-love. She thinks, it derives from, it operates together with ideologies and logics of violence toward humans.??
I return to tracking the former US ambassador Patricia Butenis, but this time in Iraq. Tracking is now virtual, made much easier by the internet and its search engines.
Killing Iraqis
?
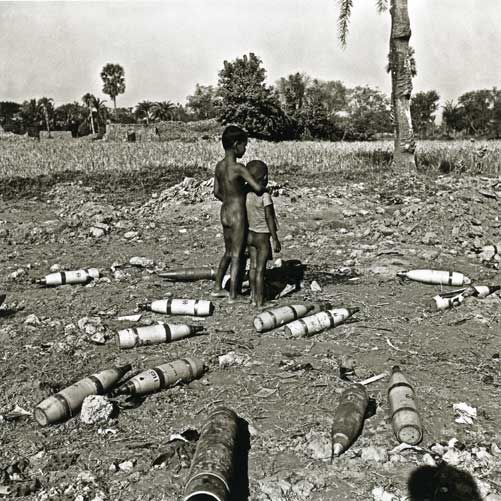
Baghdad – Mohammed Hafidh says he refused to accept an envelope filled with $12,500 in cash from Patricia Butenis, deputy chief of mission at the US Embassy in Baghdad, as compensation for the death of his 10-year-old son, Ali.?
?I told her that I want the courts to have their say,? says Mr. Hafidh, whose son was among 17 Iraqi civilians killed in a Sept 16 shooting involving Blackwater USA security guards ? private contractors who were escorting a US diplomat at the time.???
Haythem al-Rubaie, who lost his son and wife in the same shooting, says he won?t even meet with Ms. Butenis, who offered cash compensation on Wednesday to seven of the victims? families, including Hafidh (The Christian Science Monitor, October 25, 2007).
I wasn?t sure I had read it right. I rubbed my eyes. Ms Butenis herself going round offering cash compensation? The deputy head of mission herself? And I, in my utter na?vet?, had thought suchlike duties were performed by CIA officials. A?Washington Post?story helped explain matters: the Nisoor Square massacre had sparked outrage in Iraq. The embassy offers were unusual but reflected ?the diplomatic and political sensitivities raised by the shootings.? Hmm, I thought, rather quaint language. You wouldn?t think they were talking of massacres.
The Post story provided further information. A State Department official had asked Haitham (name differently spelt) what he thought was fair compensation for his wife and son. He had replied, ?They are priceless.? On being pressed, he had said, ?Like Lockerbie.? The families of victims of the Pan American bombing over Scotland had reportedly received $8 million dollars in compensation from the Libyan government. He had added, ?And you would have to deliver the criminals to an Iraqi court just like Libya delivered the criminals to the British.???
Being appointed the second-in-command of the Baghdad mission was undoubtedly a promotion. But being there sounds rather wretched, what is the English phrase? It?s a dog?s life…
War diplomats
?
US diplomats would seem to agree.
?State Department employees serving in Iraq get their full salary plus 70% differentials for danger and hardship service. Got a family living in, say, western Europe as part of your last assignment? No problem. The State Department says they can stay there in housing provided by the government as you serve in Iraq. Or, if you like, move the family to a U.S. location of your choice with an allowance that comes on top of the other financial incentives. And for those Foreign Service strivers thinking of a posh future post in some place like London, Paris or Madrid, keep in mind that State Department employees who volunteer for Iraq are now guaranteed one of their five top picks for the next assignment following Iraq. And the U.S. embassy and Baghdad definitely wants you to know that Iraq duty will do you well in promotion consideration down the road? (Times, November 5, 2007).
But the perks were not enough. Forty-eight positions remained vacant. Late last year, the State Department was forced to issue a warning to more than 200 officers. Unless they volunteered, they would be forced into ?compulsory Iraq se
rvice.? Since then, 15 individuals have come forward, but 33 spots still remain vacant.?
I was amused. Not many seem to have been taken in by the US secretary of state Condoleezza Rice?s idea of??transformational diplomacy??(January 18, 2006). ?We must begin to lay new diplomatic foundations to secure a future of freedom for all people.?
Wanted: dogs of war
The United States has always wished that Bangladesh take part in the Multi-National Force in Baghdad. We have always welcomed Bangladesh?s participation. But, [Butenis] added, the people internal to Bangladesh, the common people of Bangladesh are against the idea. It is a difficult decision for Dhaka. Had Dhaka been asked? Butenis did not give any clear-cut answer (Manab Zamin, March 4, 2008).?
In English, ?dogs of war? is an archaic term for soldiers, coined by Shakespeare. ?Cry ?Havoc!?, and let slip the dogs of war? (Julius Caesar, Act III, scene 1, line 270).???
The US needs dogs of war. Bangladeshis will not agree to their armed forces joining American-led occupiers in Iraq. Not in their name, no. But there may be other ways. Talk of?setting up a Muslim UN peacekeeping force?has been gently circulating for the?last couple of years. At some stage, that will probably be voiced as a compromise solution. Everybody will heave a sigh of relief. US forces will hunker down in?US mega-bases in Iraq, they will lead safe lives of occupation. Less body bags to be shipped home, while UN peacekeepers from moderate Muslim countries like Bangladesh maintain peace above ground.
If it so happens, they will be the dogs of war in an imperial occupation that has ravaged the cradle of civilisation.
First published in New Age 17th March 2008


























 Jyotirmay Guhathakurta and Basanti Guhathakurta with seven year old daughter, Meghna and nephew Kanti in Gandaria, Dhaka, 1966. Bangladesh.
Jyotirmay Guhathakurta and Basanti Guhathakurta with seven year old daughter, Meghna and nephew Kanti in Gandaria, Dhaka, 1966. Bangladesh.  Choles Ritchil. Photographer unknown
Choles Ritchil. Photographer unknown Mutilated body of Choles Ritchil. Photographer unknown
Mutilated body of Choles Ritchil. Photographer unknown Cleaners clearing debris outside the Rangs Building to make way for traffic. Early hours of the morning. 8th December 2007. Dhaka. Bangladesh. ? Zaid Islam
Cleaners clearing debris outside the Rangs Building to make way for traffic. Early hours of the morning. 8th December 2007. Dhaka. Bangladesh. ? Zaid Islam Demolition workers who have set up their own emergency team, warm themselves at night. 8th December 2007. Dhaka. Bangladesh.
Demolition workers who have set up their own emergency team, warm themselves at night. 8th December 2007. Dhaka. Bangladesh. 










