Aid – Bangladesh / WORLD OF MONEY
When you have too much money what else can you do except go to a swimming pool to show off, to say ‘Look at the money I have – I go swimming in a big hotel’s pool.’ The rich and their airs! Coming out with their cars just to show off to us, to the poor, to those of us who don’t have cars. The way they look at us! And their talk: which is better, a white car or a black car? It’s unbelievable, the arrogance!
Advert We are poor. But the fact that we have cameras and know how to take photos makes people uncomfortable. And so something simple becomes complicated. People who see us keep asking us ‘Accha, are these the cameras you use?’ But, you see, the camera’s not the point. The point is to take photographs. It doesn’t sit well with a lot of folks that the children of the poor should have cameras. Makes you laugh. Once Bhai’ya took some of our shots to the Lab for printing. The people at the Lab thought that one of the photos was his. ‘Take a look at Shahidul Alam’s work,’ they said. Well, it was actually taken by Iqbal, and when Bhai’ya told them so, they just shut up and wouldn’t say anything more.
Hamida and Rabeya have been abroad. The word has spread. That’s how they are introduced, as having gone abroad. We take photos. That is not our identity however. The point is who has gone abroad. Yet another way to show off is English. You aren’t anybody if you don’t know English. As if the real thing, the only thing, is not the work itself, but whether you know English. It’s such a fashion to speak it. They say you have to know it, but what do the foreigners know? Shouldn’t all those photographers and all the other visitors who come here know Bangla? Nobody tells them ‘You should know Bangla’. Through our photographs we want to change things. But lately the going has been tough. With the children of the wealthy it is enough that they take photos, but with us it seems that we have to prove ourselves by learning English too. What will happen to those English-speaking friends who also carry on the struggle? Will they learn our language and join us? Oh come on! Will they not join ranks with us? What then is our language of photography to be? These comments were made during an informal discussion involving |
Tag: Shahidul Alam
The War We Forgot
Subscribe to ShahidulNews
![]()
Iqbal had asked me when we first met. “Bhaiya, where are Barkat and Salaam’s graves?” I didn’t know. He was 10, I was 39. As a 15 year old in 1971, I had felt the warm flush of victory as I held a Pakistani Light Machine Gun in my hand. I hadn’t really won it in battle, but only recovered it from a burning military truck. But the joy was just as much. That was the time when a rickshaw wallah had refused to take my fare, because he had heard me greet a friend with ‘Joy Bangla’ (freedom for Bengal, the 1971 slogan symbolizing freedom from Pakistani rule). Things had changed, and the promise of our own land had slowly been eroded by politicians and military rulers who had lived off our dreams. Each time we became skeptical, each time we sniffed that something other than ‘Shonar Bangla (Golden Bengal)’ was in their minds, they led us on with vitriolic rhetoric. Eventually, as on that day in 1994, I too had forgotten. I didn’t know where Salaam and Barkat’s graves were. I had never heard of Dhirendranath Datta. More importantly, I didn’t care. But Iqbal did. Born long after Salaam and Barkat’s bodies had merged with the soil, Iqbal only knew of this great battle that we had fought. Though the heroes had changed depending upon who ruled the country at any particular time. Salaam and Barkat were beyond dispute. They were not a threat to anyone. They didn’t apply for a trade license, or bid for a government tender. It was safe for the history books to remember them. Remembering Hindus or women was a bit more problematic.
My search for these other heroes, the ones with cameras, began in 1994. After Iqbal reminded me that I had forgotten. It was in the Paris office of Sipa that Goksin Sipahioglou, excited at my presence ran down the stairs and brought back with him an armload of slide folders. It took a while for it to sink in. These were the first colour photographs of the Muktijudhdho that I had ever seen. We had heard that some of these photographs had been published. But our only source of news at that time was Shadhin Bangla Radio. It talked of the glory of our freedom fighters, of how they were fearless against enormous odds. Of their glory in battle. M R Akhtar Mukul in ‘Chorompotro’ was the one voice we longed for. We chuckled as he talked of the plight of the Pakistanis. His wry but animated voice, muffled by the blanket we hid under, and barely audible in the turned down volume of the transistor radio, gave us hope, and kept us going through the dark nine months.
It was Abbas’ photographs that Goksin had brought for me. Later that month, in the back garden of a house in Arle, I met Don McCullin. Don was excited about the show I wanted to do, and unhesitatingly agreed to give us pictures. I found Abbas, at a beach near Manila, quite by accident. Both of us had been following the golden late afternoon light in a summer evening in Manila beach. Abbas too was excited. He wanted to be part of the show. Michele Stephenson and I had been in the same jury of World Press Photo on two occasions, and I had plenty of time to tell her about my plans. She invited me to New York and arranged for me to go through the archives of her magazine, Time. It was in the basement of the Time Life Building in the Avenue of the Americas, that I came across the daily bulletins that the reporters had sent in.
Memories flooded through my mind as I remembered those harrowing days and nights. I remembered the screams of people being burned alive as the flame throwers belched fire at the Holiday office near the Hotel Intercontinental.
Most of the people who died were the people who slept in the streets and the slum dwellers around the newspaper office. Those who chose to escape the fire ran into a hail of machinegun bullets. My father, mother, Babu bhai and I, watched quietly from our verandah in Nasheman on New Elephant Road. My dad had suffered from Hindu bhodrolok prejudice in the pre-partition days, and had never supported the break-up of Pakistan. And we would have great fights in the home, the younger ones wanting independence, Dad’s generation feeling things could be patched up. That was the night Dad said it was over. No longer could we ever be one Pakistan.
I excitedly went through the reams of paper. Each scrap of news had a meaning for me. I could relate to these news bulletins. I remembered the horror of those nights. As I thumbed through a tattered red diary, I noticed the skimpy notes of a photojournalist as he traveled through Jessore. I remembered Alan Ginsberg’s poem. It was David Burnett’s diary. Several years later as David and I met in Amsterdam in yet another World Press Jury, I told him where his diary was. In Kuala Lumpur, Dubai, Delhi, and so many other cities have I picked up the scraps of evidence that would help me piece this jigsaw together.
It was in Paris that I spoke excitedly of my plans to Robert Pledge, the president of Contact Press Images. Robert shared my enthusiasm for the project, but I harried him with my feverish frenzy. We couldn’t wait, we had to do it now. That now has taken over six years. But in these years we have made the most amazing discoveries. The stories, the images, the people we have come across, make up the life of this exhibition. It is the war veterans, the men and the women in the villages of Bangladesh, who fought the war, the forgotten heroes with their untold stories, the men and women who were killed and maimed, the women who were raped that this show is dedicated to. It is not a nostalgic trip for us to romanticize upon. It is for Iqbal and his friends to know that Barkat and Salaam, were more than simply names in history books.
Shahidul Alam
November 2000. Dhaka
When a Modem Costs More Than a Cow
Bangladesh’s history is that of colonisation, oppression and genocide. It is less than thirty years since several million people were killed and many more became refugees in perhaps one of the greatest atrocities of modern times. There were two basic tools that have engineered and enforced this domination, technology and language. Our war was based on language, and it was technology that provided the military, the muscle.
With technology and language both being owned by the wealthy, class divides are intrinsically linked to this hegemony. How then do we see the most dominant of modern cultures, the Internet? The ownership of the Net is almost entirely Northern globally, and exclusively urban and elite locally. The hype surrounding the Internet and the top down approach with which it is meant to provide deliverance, hides the politics of corporate ownership, the way in which this media is controlled, and the simple fact that for the majority of the world the Internet doesn’t exist, and for many others in the South, it is barely effective.
The propaganda surrounding this imperialist tool, fits in well with the stated objectives of our colonial rulers: ‘ Natives must either be kept down by a sense of our power, or they must willingly submit from a conviction that we are more wise, more just, more humane, and more anxious to improve their condition than any other rulers they could possible have.’ ?Minute by J Farish dated August 28, 1838, quoted in B.K.Boman-Behram, Educational Controversies of India, p. 239
Language forms the biggest barrier to computer literacy in Bangladesh, and when less than 15% of the population has access to electricity, and a far smaller fraction owns computers, it is clear that only the wealthy will have access to this technology. Here, a modem costs more than a cow. Yet this technology and this associated language both exist. We must stare this dual hegemony straight in the face, but we cannot, dare not, let this technology pass us by. To find creative routes to turn this technology to our benefit is our greatest challenge.
The Internet can be a subversive tool. It remains the only medium which gives scope – relatively inexpensively, and without the support of the gatekeepers, for a lone voice to be heard. It is this unique characteristic that we have to nurture. The bigger players have the money, the clout, the physical strength and the social control to bludgeon their way through, but they do not have the flexibility, the ability to pop up and disappear at will, the speed of action or the elasticity to slip through the holes, that the well trained individual has. Given the important proviso of access, the Net is fast, cheap, and difficult to stop. It is the Net that we must use, to fight its own dominance.
Cultures dominate by creating norms that are not questioned by creating ‘accepted practices’ that become tools of oppression and by defusing the need for critical analysis. Consumer forces convince us of the need for bigger RAM, faster processors and software that gives us greater choice. Wildly disproportionate pay scales, between locals and expatriates and between English speaking and non English speaking co-workers teach us the importance of fluency in English. Indecent consultancy fees that siphon back most of what is provided as aid, make us believe that western values and skills are what one must strive to attain. Dominant cultures define who is primitive and who is civilized. The dissenting voice that questions the goodness of donor efforts, quickly discovers the reach of donor funds. One must not stand in the way of progress, particularly when that progress is backed by individuals whose personal wealth is greater than that of entire nations they are trying to civilise.
Now we are to behold a literature so full of all qualities of loveliness and purity, such new regions of high thought and feeling? that to the dwellers in past days it should seem rather the production of angels than of men. Madras Christian Instructor and Missionary record (1844) Let us examine these ‘productions of angels’ in Bangladesh in greater detail. Networking has traditionally been a strength of global organizations, multinationals, international donor agencies and NGOs, and large local NGOs. International telecommunications has been way beyond the means of small local players. Even interconnectivity amongst themselves has often been too difficult to maintain.
It was to address these specific issues that Drik set up a small Email network in 1994. Our server was a used 286 computer, and the phone line was shared for voice, fax and data. We used Fidonet, and rang Amsterdam (our gateway to the Internet) only twice a day, but even that transformed the way we worked. Our clients included large and small NGOs, government ministers, western embassies, The World Bank, students, corporations, activists. There were frequent power cuts, the telephone lines didn’t always work, a thunderstorm destroyed most of our modems, and we ourselves were only semi-skilled. Still our network grew. And though we were paying our Dutch counterparts 30 cents per kilobyte for transmitting files, we were making the system pay. We setup fax gateways, and an Email club where more experienced users taught the others how to use Email to extract information from the net, how to compress files to save on transmission costs, and how to decode files that looked like garbled messages.
Our oldest user, photographer and writer Golam Kasem, had just turned 103 and had never seen a computer before. I would cycle over to his house in Indira Road with a printout of a message from his grandson in Canada and next day peddle up to collect his reply. I remember the frail old man, straightening up the computer printout and adjusting his thick glasses as he held the paper by his tungsten lamp. Bangladeshi feminist writer Taslima Nasreen received a death threat from Islamic fundamentalists and was charged with blasphemy by the Government. We needed to move quickly – to create national and international pressure so Taslima could come out of hiding to alert friends overseas, PEN (the international writers support group) and Amnesty International and the campaign took off. Our fragile network was working.
There were other ways in which the technology was being used. The Daily Star newspaper set up a ‘Live from the Internet’ column. Readers who had no access to either computers or the Internet would write to the Star, which the newspaper would relay to Internet chat groups. The responses would get printed in the column. These hybrid off-line techniques became an important means for our communication. We setup electronic bulletin boards and a whole set of discussion groups sprang up. Important campaigns were initiated through these virtual conferences, and the network became a seat of resistance.
When full Internet services became available however, networks such as ours were quickly ditched. The government ignored us and gave permission only to large corporations and major NGOs. Interestingly, Grameen Bank, BRAC and Proshikha, three giant NGOs who used to get connectivity from us, set up their own ISPs. In Bangladesh, they owned the Internet. The conferences disappeared, and local networks that we had painstakingly setup rapidly vanished. We were being squeezed out of the market. Unable to compete at an economic level we found alternative means for providing support to our users.
The ISPs were not interested in servicing non-urban users. We maintained our off-line service, which could still service people with DOS based machines, with analog lines, living in remote areas. We leased lines from these NGOs and used them to transfer data to the Net, reducing our transmission costs. We began setting up new discussion groups and mailing lists. Most importantly, we set up our own web site, which we used to support our campaigns. We moved from providing connectivity which we could no longer provide reliably, to providing content.
Recently, when women students at a nearby university began a campaign against campus rape, our web site became a principal tool for advocacy. Pressure that was exerted internationally and nationwide added to the massive physical protests by the students forcing the establishment to conduct an enquiry. Five students of the ruling party were indicted. At it’s peak, our site was getting over 5000 hits per day. Articles were sent to the newspapers, and we began publishing things they had censored out. We were learning to wield our new weapon. We had been concerned by absence of working class and rural representation in mainstream media.
At about the time we set up our Fidonet network, we began providing photojournalism training to working class children. The going was never smooth and we made many mistakes, but these children progressed remarkably.
Excited by what the children had achieved, we tried setting up a distance education programme for rural Bangladeshi children. We set up a server in a town called Sylhet in the North East of Bangladesh. Using microwave links we then connected schools in nearby villages (using computers bought collectively by students and by us) to the server, A dial up link to Dhaka provided Internet mail. Sylhet has a lot of migrant workers who have gone overseas, and Email reunited these families. We are now helping develop multimedia training modules for teaching vocational skills. We tried linking the education programme with an afforestation scheme and even tried setting up a commercial service that would help subsidise the project. Things didn’t work as well as we had planned, but enough progress was made to interest other players in the project.
The focus however already seems to be shifting from the basic grass roots work that we had set out to do. Now that the big boys are interested, the transformation they may bring, might have the same effect as the changes they introduced to the Internet scene. A major cause of the high connectivity costs in our region is the monopoly of the telecom sectors in all our countries. This is not merely a national issue, but is linked to the unequal trade terms between nations of the South and the North. Alliances between global telecom players and local governments have resulted in local consumers getting shortchanged.
Vested interests have often required entire nations to follow technological solutions totally unsuited to local requirements. We began using the Net to pool together a team of regional IT professionals. We pleasantly discovered that our collective knowledge base could easily cut through the hogwash that the governments and corporations used.
The other useful collective decisions we were able to make related to developing local language tools, from standard UNICODE formats to OCR for local languages. Since many of our languages have common roots we found that work being done by several people across local borders could provide a lot of synergy. An area that has to be addressed, particularly where the international donor community is involved relates to the mind set that ‘appropriate technology’ is necessarily ‘low technology’. It is fashionable to design ergonometric rickshaws, and better spinning wheels. When we talk of Internet or IT there is the feeling that it is inappropriate for poor people and cannot have a role in ‘poverty alleviation’.
It is important to recognize that poverty cannot be addressed unless one addresses exploitation and distribution modes within society. This applies not only to regional power relationships but also to global imbalances. Politicians rarely feel accountable to voters and hide behind the lack of transparency of the government sector. Major decisions that affect community life are taken behind closed doors, where the people most affected have no access. Though the constitution grants equal rights to all citizens, legal, medical and educational rights are only realized for the minority in power, with women and children of poor communities, pegged at the other end of the spectrum, rarely aware of these rights, let alone being in a position to extract them from society.
Where information is power, denying information to marginalized communities, actively prevents the rural poor from overcoming the unequal power structures that they are trapped within. While it is in the interest of the powerful in society to restrict such access, it is also in the interest of the powerful nations to deny access and maintain domination. The unrestricted flow of general information is an essential pre-requisite for an egalitarian society
Shahidul Alam
Dhaka, 30th April,1999
Thank You Mr. Harkin, Sir!
Subscribe to ShahidulNews
![]()
When US Senator Tom Harkin proposed a boycott of the products of child labour,
Western campaigners applauded. But there were unforeseen consequences
for the children of Bangladesh, as Shahidul Alam reports.
No. No photographs. Saleha is scared. Many a time she has hidden under tables, been locked up in the toilet, or been sent to the roof in the scorching sun for two or three hours. It happens whenever foreign buyers enter the factory. She knows she is under-age, and doesn?t want photographers messing things up ? she needs the job. The whole industry has suddenly become sensitive. Owners want their factories open. The workers want their jobs. The special schools for former child labourers want aid money. No photographs.
Neither Saleha nor any of the other child workers I have interviewed have ever heard of Senator Tom Harkin. All they know is that pressure from the US, which buys most of Bangladesh?s garments, has resulted in thousands of them losing their jobs at a stroke.
According to a press release by the garment employers in October 1994: ?50,000 children lost their jobs because of the Harkin Bill.? A UNICEF worker confirms ?the jobs went overnight?.
The controversial bill, the ?Child Labor Deterrence Act?, had first been introduced in 1992. A senior International Labour Organization (ILO) official has no doubt that the original bill was put forward ?primarily to protect US trade interests? ? Tom Harkin is sponsored by a key US trade union, and cheap imports from the Third World were seen as undercutting American workers? jobs. ?When we all objected to this aspect of the Bill,? says the ILO official, ?which included a lot of resistance in the US, the Bill was amended, the trading aspect was toned down, and it was given a humanitarian look.? It was when it was reintroduced after these amendments in 1993 that the Bill had its devastating impact in Bangladesh.
The child workers themselves find it particularly hard to interpret the US approach as one of ?humanitarian concern?. When asked why the buyers have been exerting such pressure against child labour, Moyna, a ten-year-old orphan who has just lost her job, comments: ?They loathe us, don?t they? We are poor and not well educated, so they simply despise us. That is why they shut the factories down.? Moyna?s job had supported her and her grandmother but now they must both depend on relatives.
Other children have had no alternative but to seek new kinds of work. When UNICEF and the ILO made a series of follow-up visits they found that the children displaced from the garment factories were working at stone-crushing and street hustling ? more hazardous and exploitative activities than their factory jobs.
?It is easier for the boys to get jobs again,? Moyna complains, pointing to ex-garment boys who have jobs in welding and bicycle factories. Girls usually stay at home, doing household work and looking after smaller children; many end up getting married simply to ease money problems.
Rethinking
In the wake of the mass expulsion of child garment workers it was plain that something had gone very wrong. UNICEF and the ILO tried to pick up the pieces. After two years of hard talking with the garment employers they came up with a Memorandum of Understanding. This guaranteed that no more children under 14 would be hired, that existing child workers would be received into special schools set up by local voluntary organizations and would receive a monthly stipend to compensate them for the loss of their wages.
Some garment owners feel that, instead of doing a deal, they should have called the US bluff and continued employing young children. ?We export 150 million shirts a year to the US,? says one. ?The K-mart $12 shirt would have cost $24. Bill Clinton would have lost his job.?
As of now 10,547 of the estimated 50,000 children have been registered, and of these 8,067 have enlisted in school. Most weren?t registered initially, as few garment owners admitted having children working in their factories. Many lost their jobs before the registration process began. Unregistered children, regardless of their age or their schooling, are not admitted into the scheme.
Saleha is tall for her age. Though in her factory there are quite a few under-age children, in most factories children that look small are no longer taken. This is what Moyna and Ekram and the other children repeatedly say: ?We didn?t make the size.? In a country where births are not registered there is no way of accurately determining a person?s age. Children with good growth keep their jobs. Children who look smaller, perhaps because they are malnourished, do not.
The reliance on size rather than age means that many children are still at work in the factories ? and many have no inclination to take up a place in one of the special schools. Take Sabeena. Her factory is colourful with tinsel when I visit and many of the girls have glitter on their faces. It is the Bangla New Year and Eid all in one and they are celebrating. Sabeena proudly shows me the machine she works on. She is almost 14 and, like Saleha, big for her age. She has been working at a garment factory ever since she finished Grade Five, about 18 months ago. Until then, schooling was free. There was no way her parents could pay for her to go to school and, with her father being poorly, Sabeena needed to work to keep the family going.
Taking home 2,200 taka ($52) a month (with overtime) Sabeena, at 13, is now the main breadwinner in the family. She is lucky to have work, though she would rather study. She laughs when I talk of her going to school. She has mouths to feed, and to give up her job for a 300-taka-per-month stipend for going to school simply wouldn?t make sense. Besides, the special schools only teach up to Grade Five. The better students, who have studied that far, find they have neither jobs nor seats in the school. So Sabeena?s studies begin at around eleven at night, with a paid private tutor, usually by candlelight. At seven in the morning she has to leave for work. Seven days a week.
Money is a key concern even for those children who have been received into the special schools. At the school run by the Bangladesh Rural Advancement Committee (BRAC) in Mirpur, the children gather round a worker doing the rounds. ?When do we get paid, sir?? they keep asking.
Despite the promises, not a single child that I have interviewed has received the full pay they are owed. In some cases field workers, eager to improve their admission rates, have promised considerably more than the stipulated 300 taka ($7) per month. In others, unfounded rumours have created expectations that the schools cannot meet.
Shahjahan (pictured on the facing page) was one of the lucky ones admitted to a BRAC school. The 300 taka per month is a small sum for him too, but he works in a tailoring shop from nine till eleven in the morning, and again from two-thirty in the afternoon till ten at night. He doesn?t complain. Though the scheme does not encourage it, he feels he is getting the best of both worlds: free schooling, including a stipend, as well as paid work and a potential career.
A strange question
Did they like working in garment factories? The children find this a strange question. They earned money because of it, and it gave them a certain status that non-working children did not have. They put up with the long hours. The exceptions remind me that it is children we are talking about. ?I cried when they forced me to do overtime on Thursday nights,? says Moyna. ?That was when they showed Alif Laila (Arabian Nights) on TV.?
Child workers are popular with factory owners. ?Ten- to twelve-year-olds are the best,? says Farooq, the manager of Sabeena?s factory. ?They are easier to control, not interested in men, or movies, and obedient.? He forgets to mention that they are not unionized and that they agree to work for 500 taka ($12) per month when the minimum legal wage for a helper is 930 taka.
Owners see Tom Harkin as a well-meaning soul with little clue about the realities of garment workers? lives. ?As a student, I too hailed the Bill,? says Sohel, the production manager at Captex Garments. ?I was happy that someone was fighting for children?s rights. But now that I work in a factory and have to turn away these children who need jobs, I see things differently. Sometimes I take risks and, if a child is really in a bad way, I let them work, but it is dangerous.?
The notion that a garment employer might be helping children by allowing them to work may seem very strange to people in the West. But in a country where the majority of people live in villages where children work in the home and the fields as part of growing up, there are no romantic notions of childhood as an age of innocence. Though children are cared for, childhood is seen as a period for learning employable skills. Children have always helped out with family duties. When this evolves into a paid job in the city neither children nor their families see it as anything unusual. In poor families it is simply understood that everyone has to work.
The money that children earn is generally handed over to parents, who run the household as best as they can. Most parents want their children to go to school. But they also feel that schooling is a luxury they cannot afford. The garment industry has increased the income of working-class families in recent years and this has also led to a change in attitudes. Many middle-class homes now complain that it is difficult to get domestic ?help? as working-class women and children choose to work in garment factories rather than as servants. This choice ? made on the grounds not just of better economics, but of greater self-respect ? is one many children have lost because of the Harkin Bill.
The US is wielding power without responsibility. A nation with a history of genocide and slavery, and a reputation for being a bully in international politics, suddenly proclaims itself a champion of people?s rights, but refuses to make concessions over the rates it will pay. The dollar price-tags on the garments produced in some factories suggest a vast profit being made at the US end. The buyers claim that what they pay for the garments is determined by ?market forces?. The garment owners make the same claim with regard to the conditions of employment for their workers. Both are simply justifying their own version of exploitation ? and to address child labour without addressing exploitation is to treat the symptom, not the disease.
The garment-industry experience has led to an active debate amongst development workers and child-rights activists. ?What we have done here in Bangladesh is described as fantastic,? says a senior ILO worker. ?I wonder how fantastic it really is. How much difference will these two or three years in school make to these children? In three years, the helper could have been an operator, with better pay and more savings. Even if the manufacturers keep their word and give them back their jobs at the end of their schooling, the Memorandum children will hardly be better off, while their peers will have gotten on with their careers. We have spent millions of dollars on 8,000 children. The money itself could have transformed their lives. This is an experiment by the donors, and the Bangladeshi children have to pay.?
The children?s names have been changed to protect them.
Online Lifeline

Third World activists are using global connections to pressure the powers-that-be and even save lives.
Bangladeshi photographer Shahidul Alam has little doubt about the subversive potential of the Internet in his country.
Come out, we won’t shoot. The sound of a police megaphone jolted us to attention. After they left our little flat in Dhaka I went up to the roof to try and find the person they thought we were hiding. I found no-one, but the raid made us realize that the nine-year-old dictatorship of General Ershad was feeling the pressure.
Running Drik, a photo library set up to promote a more positive view of developing countries, we were already in the business of disseminating information. Up to this point we had managed quietly to distribute our photographs abroad through helpful friends. Now the need was more urgent: we had to prevent further bloodshed. We couldn’t phone or fax since none of us had an overseas line. Two days later in December 1990, when General Ershad did finally step down, we began collecting the money for the line. Continue reading “Online Lifeline”
Abba
It was the first rain of the year, the end of winter. I hadn’t noticed the weather till then. The previous week had been one of turmoil and discovery. I had spent hours watching my father’s face, looking at the lines in his hands, the fingernails. The shape of his toes. Never before had I noticed the little cleft at the tip of his nose, which I too had. His eyebrows were thick, bush and soft. The doctors had told us it would need a miracle but we clung on. Abba had been very clear about how he wanted to leave. There were to be no heroics. No expensive treatments, no trips abroad, above all, he had not wanted to live a life where he could not be fully active. On the second day in the hospital, the doctor suggested that I ask my sister who was a doctor in the UK, to come over. The implications were obvious. She might never see him again. There was a national strike in the country, in protest against a one-sided election. Rahnuma’s brother Saif, arranged for an ambulance to get my sister from the airport to the hospital. She wept and he smiled as they met.
Those few hours were lovely, despite his condition. We talked of politics, his flowers, of his grandkids. He was furious with the government for staging a mock election and wanted to know what was going on in the streets. Then the breathing got heavy and they put on the oxygen mask. Late at night, the doctor asked if we agreed with putting him on the ventilator machine. There was a risk attached, but she felt it was our only realistic chance. It needed a move to another building. He was for the first time unsure of what was going to happen. I held him tight in the ambulance. Making sure he knew I was constantly there. In the surgical ward, they were going to pump him with morphine so he wouldn’t resist as they pushed the tubes down his throat. Between gasps I saw his eyes scanning the room, looking for a familiar face. I called out gently, and the eyes rested as they met mine.

When A Pixel Paints A Thousand Words
Subscribe to ShahidulNews
When A Pixel Paints A Thousand WordsI remember my fascination with Charles Babbage's machine, and my inward fear when first given the chance to use a computer. Logging in to the VAX was a great thrill, but that was the day of punch cards, and writing programs for everything. Learning was a slow process. A young kid told me of a program he had written. It was a simple program in basic that merely printed on the screen "This is my first program," but I was impressed. Boolean numbers were the next marvel. Soon I was changing things, making things happen. I worked with computer models. Intermediate structures of molecules I was synthesising in a chemical laboratory. A Tektronix monitor allowed me to see the shapes of the nucleotide rings that I worked with. I stretched bonds, distorted angles, looked for conformations of low and high stress. Almost listening to my molecules scream as I bent them into painful configurations. Watching them relax as I discovered the lowest energy states.
The printout churned out numbers, hundreds of them. These were what I needed for my quantification. Figures that I could translate into bond energies for transition states, numbers my examiners would understand. What fascinated me was that by changing numbers I could look at my molecules differently. I would change the window size, the azimuth angles, rotate them, look at them from above and below. I was like a little child with a giant model hovering above me that I could twist and turn at the press of a button. The computer and I had made friends.
I remember the excitement my father had when I bought my first computer. He had been a scientist all his life, but had to adopt an administrative role to achieve much of what he had done. He was an artisan who had wanted to work with his hands and his mind and sad that much of modern technology was passing him by. He was like a child in front of the machine. We watched together in amazement as the printer rattled out text noisily. I remember coaxing my partner Rahnuma into trying out the computer. She was convinced "the computer would bite." I remember sharing her deep sorrow when all her work got accidentally deleted. I remember the joy of adventure as the technician searched the disc for disjointed bits of information, trying to make a patchwork file out of her lost data. I remember feeling sad when my first motherboard died.
I got my video digitiser as compensation from someone who had lost one of my books. My friends and I couldn't get it to work, but the thought of animated images being created and manipulated in the computer and then transferred to video, got our imagination soaring. The next major event was my friend buying a hand held scanner. Soon I had bought one, and the next few weeks were merrily spent dithering, sharpening, solarising. I tried, without too much success, repeating some of the things I had done in the darkroom. My excitement had been blunted. Though there was the joy in discovery, I was expecting too much. The first darkroom I had worked in was cold, Spartan, and very large. I remember dancing in the room when the first black and white print emerged. I still feel that tingling joy when the first shadow details begin to emerge on the wet paper glistening in the red muted safelight. The computer image forms section by section, each bit complete and unchanging as the whole forms. I miss seeing it happen, breathing on the developer, rubbing furiously to darken a hot spot, willing the print on when the blacks aren't rich enough. Perhaps there is something about that slow process of making masks, the uncertainty of the outcome, the sheer joy of seeing a full range of shimmering tones that will never be replaced. But curiously, with so many tools at ones disposal on the desktop, it is as if my imagination and not my tools which is the limiting factor.
When I teach about colour, I tell people to close their eyes and think of a colour they have never seen. Neither I nor they have ever succeeded. We are so limited by our experiences. I believe that is what we should try and overcome. All these tools are darkroom based. Things people have done mechanically in some form or other.
What I would like to do is to be able to visualise what I have never experienced. Not some darkroom trick made easy, not yet another combination from a million and a half palettes. I would like to see the world as I might after I was dead. Or perhaps through the eyes of a giant caterpillar, with its UV vision and its huge towering compound eyes. I would like to see as a lover sees through joyous and tear streamed filters.
Digitising things is in a way like breaking things that we know and perceive — elephants, numbers, colours, sounds, loved ones — into elemental particles that are within the group identical, sexless, classes, and nondescript, surviving almost as conceptual entities. Our universe defined as electrons, mesons, pions. These characterless wave particles, by virtue of their collective structure, make up blades of grass, Einstein's and Mohammed's, shafts of lightning, our thought processes. In digitising words, numbers, graphic, sounds, colours, we convert all these objects of our perception to strings of 0s and 1s. The ultimate deconstruction. A scream, an iridescent hue, an irrational number, all translate to 0s and 1s.
Is that the goal of technology? The search for the ultimate truth? The oneness we so long to find? Is that what our genes perpetuate — 0's and 1's? What a let down for our romantic dreams. What a wonderful discovery. What staggering simplicity. Just two building blocks, a zero and a one.
Sitting at my terminal I feel the cool breeze of the monsoon afternoon, heavy with the sweet scent of ripe mangoes. A crow calls from the coconut tree, the call fighting for recognition amidst the ever rising clamour of the construction workers building yet another sky scraper. The soft cold light from the textureless grey sky bounces gently from the green leaves. The keyboard makes a quiet clatter as my cursor moves across the screen. WYSIWYG. Is this reality? Or has David Hume's immateriality found a new meaning. There is no you or I, or the universe or God, just 0s and 1s.
I print my pictures full frame. In a way exercising a certain discipline upon myself to be rigorous about what I include, and exclude. In a way to accept the accidents that take place, the elbow in the corner, the dismembered torso, the blur of a passing stranger, the obstruction of a carelessly outstretched limb, the bit we didn't really want to show. The certain grace of serendipity that is difficult to replicate. I shoot on roll film, and therefore do not have the preconceived notions of zones, that my fine art colleagues espouse, I do not give N- 1 development and N+ 2 exposure, unless it is for the whole shebang.
I am easily seduced by the dark rich tones of a juicy print. I like my catch lights clean and sparkling highlights with a hint of texture. I like subtle detail in my shadows. I try to capture what is and create what isn't. In no way do I attempt to simulate "what there was." The myth of objective perception never moved me.
My print is at least as much a product of my values, my desires, my moods, my ability , as it is of the physical entity that gave rise to it, and I have never been ashamed of it.
So what is this representation of reality, this myth that a photograph never lies? A photograph is a tool like any other, used in whatever way its user intends, to achieve whatever end by whatever means. The faded portrait in a dying soldier's wallet is part of the reality created by him and him and us who have sent him to war. So what if the person no longer loves him, so what if he is scorned for what he does? That reality gives him courage, strength, endurance. Helps him kill others with equally faded photographs.
Wide angle b/w shots, grainy, high contrast, huge billboards with a dying malnourished child in a corner with outstretched arms. A clear message in polished bold font in the top left corner cleverly left blank. The message reads "We shall always be there." A reality constructed for and by those who want us to forget the implications. That " you shall always be there". In that role, a passive existence necessary to maintain, to nurture, the act of giving, forever and ever. A reality perpetuated and propagated, till it becomes history. Till it becomes truth. Amen.
What of the other reality? The one about how she became the way she is? The one about the outstretched arm that takes back much more than it gives? It is a reality denied.
Advertising campaigns and fund raising events forget to tell you that when you sponsor a child, you largely sponsor the players in one of the best run businesses, one called development.
Perhaps the child wasn't sad enough. The tear large enough, the halo on the giver bright enough. We now have the power. They were almost catching you with the old technology. Even though we designed things that had to be used and stored in cool dry conditions. Even though cameras cost the same as a hundred bags of rice, they were catching up. They were making statements, asking questions, interfering with reality. They will need a million bags of rice for CD ROMS and high end scanners. Our new reality is safe.
Perhaps it is all for the better. In time we will accept that pictures are the product of those who produce them and do tell lies, as do people generally. Perhaps in a more mature world wars will not be won or lost, by the media. Perhaps we will be perceptive enough not to be led into a war that has always been present. Perhaps like Jonathan Livingston Seagull, we will really learn to fly. Like Maxwell's Demon we will tame the pixels and teach them to dance.
But for any of this to happen, this digital revolution must reach out to those who have always been denied. We must dance in unison.
While we unleash this flood of energy, this joy of numbers that can let our imagination wantonly soar, it must not be inaccessible to those whose reality we have always suppressed. Our gigabits and superchips must not widen the chasm that a monopolised technology already maintains. But if this was to be the way in which a little child in a village school was only a modem away. An affordable modem, like chalk and slate (still unaffordable to many). If we could paint together in a universal bulletin board. If the digital chorus included the boatman's song. If the dance of pixels syncopated with distant drumbeats. Then, surely, in a world where numbers obeyed no borders and vision was the only barrier to creativity. The new reality world belongs not only to the owners of silicon valley but to the child on the billboard.
I choose my format, use my favourite film, decide carefully on the texture of paper, without once realising that my "freedom" has always been defined by the multinationals who treat me as yet another number. Maybe I am not included in their numbers game. They publish literature that goes from 18° C to 24° C. My room temperature never goes down to 26°, but I am a buyer, and therefore I belong.
Today there is a new found freedom. I can create my own film, use Kodachrome or Fuji chrome, or the now extinct GAF 500, even my own customised brand, with a colour bias peculiar to my own taste. By changing the dot size, I simulate large format or 110 (I am already having troubled thinking outside the known formats).
Fancy software can change my perspective or magnification at will. I have Nikon's latest super lens in my armoury and even ones they haven't made.
From anamorphic lenses to ones with controlled barrel distortion, everything is in my reach. I can make pictures fuzzy, sharpen fuzzy ones. Mama take my microchip away.
It is no longer difficult to make intense highlights coexist with subtle shadow detail with ever expanding grey scales. But wasn't it the lack of grey that made Newman's portrait of Stravinsky, or Brassai's "Big Albert's Gang?" Photography's inability to retain an extreme range of tones used majestically to carve out sculptures of light in space. Surely this new technology will not tame a Newman or a Brassai. It will create new ones. The new magi, who will probe and tease, taking it to new visual heights, will ride the mighty pixel. Jerry Ullsmann's hypnotic seamless images will no longer need a master craftsman, just an Ullsmann's vision. What a test of visual puberty!
No longer will I hide my hand. My style, my approach, my visual signature will be for me to create, unfettered by manufacturers whims or market decree. What about the fight we had almost won? The one about ownership of negatives, of editorial control. Perhaps it is time to shun the obvious, the mad rush for greater circulation, the megabucks. Perhaps it is time for photographers to be their own editors.
With desktop publishing and laser printers, or even downloading page made material to high street up-market scanners, to obtain total editorial control.
A co-operative that could work as it had originally been intended, where photographs were made collectively. As for accuracy, it was always a misnomer, one's observation is always culture and context sensitive, and the photographer is no exception.
What of the photograph made out of nothing? What about painting with light? Is it photography? Surely if we can paint with light we can paint with dreams, create the morning mist or the afternoon glow. Is it a fake? Hardly. Whatever else may be false in this tenuous existence of ours, imagination is not. All that we value, that we strive to uphold, all that gives us strength, has been made of dreams, and we must dream on. If pixels be the vehicle that realises our dreams, be it so.
Perhaps the digital image will democratise photography. So many bytes per pound of flesh. Perhaps there will come a time when CD ROM costs a dollar a piece, and palm tops have gigabits of RAM. Perhaps with e-mail and electronic bulletin boards, points of view that could never before be heard will whisper in many ears, ever louder. Maybe, on the other hand, the digital revolution will create rifts within the third world itself, and limited access to an exclusive technology will widen gaps within poorer countries.
Perhaps wealth will have a greater bearing on a photographer's output than ever before.
It will no longer be the best camera and the fastest lens, but the biggest RAM and the finest peripherals which will decide. The poor will get poorer.
Perhaps that is the end result of democracy, an equality of opportunity that creates the opportunity of greater rifts. Will that rift in art, despite the natural processes of osmosis, lead to greater imbalance in society at large? Art does not have a conscience. Achievement is an end in itself that pushes it to ever extending limits. But this heightened sense of power, this endless opportunity, will need to grow a separate consciousness that will question the validity of our actions. And there is no going back. Like those Brazilian kids on the speeding trains, we must just hang on the roof, dodging the wires as best as we can, hurtling ever forward till the train stops, and just hope we are in the right station.
Chalking up Victories
Subscribe to ShahidulNews
At 17 Mozammat Razia Begum is older than most of the girls in her class at the Narandi School. She was married at 15 but her husband abandoned her.
?If I had been educated he would not have been able to abandon me so readily, leaving me nothing for maintenance,? she says. The marriage of young girls without proper contracts – followed soon after by abandonment – is a serious social problem in Bangladesh. Razia blames her parents. ?My parents were wrong to marry me off so young. If I had a daughter, I should not let her marry until she was at least 19.?
The school Razia attends is one of 6,000 non-formal village schools set up by BRAC – the Bangladesh Rural Advancement Committee – exclusively for pupils who have never started school and those who had to drop out. Three-quarters of the 180,000 pupils are girls. Although married girls are not normally catered for, exceptions are made. Many of the teachers are women: parents in Bangladesh frequently keep their daughters away from school if teachers are male. And each BRAC school is situated right in the community: if schools are far away parents will not let girls attend. It is not acceptable for girls – especially those past puberty – to walk about the countryside in this devout Muslim country.
?I am fortunate to be here,? says Razia, looking round the schoolroom with its tin roof and walls of bamboo and mud. She had to fight to come, though. Her father believes that a woman?s place is at home. ?Had I been a boy,? she said, ?my father would surely have allowed me to study.?
Razia?s own mother was married at 12 and, like her oldest daughter, had no say in the matter. ?I want my sisters? lives to be different. They should study and be given a choice about their marriage. Husbands will not dare to treat an educated woman badly.? On this subject, Razia becomes quite animated.
Razia would like to go on with her studies after she has completed the BRAC course. During the two-and-a-half hour daily session – which is timetabled to fit in with seasonal work and religious obligations – she learns literacy and numeracy, as well as enjoying activities such as singing, dancing, games and storybook reading.
BRAC have had a remarkable success in keeping the drop-out rate from their schools to five per cent and graduating 90 per cent of their students into the formal primary system. This proves that the obstacles to girls? education – even in such a poor environment – can be overcome.
As for Razia, her experience of life has forced her to question many things she once took for granted – such as the need to get married. She does not wish to marry again. And many other girls have begun to question the restrictions imposed on them. More of them want to be teachers – like their own teacher – or doctors. Razia says: ?I tell my sisters to study well and get a job. If they get a job they will be able to do as well as men and men will respect them.?
First published in the New Internationalist Magazine in Issue 240
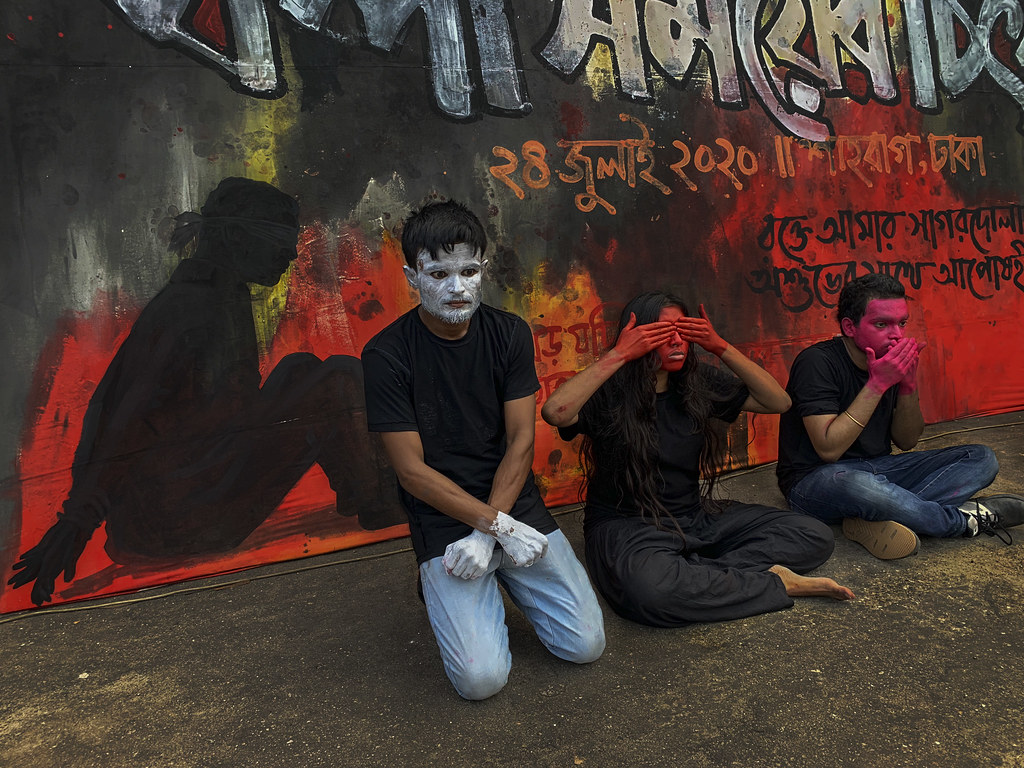

 We remember the time we had to go to some UNICEF meeting or other with Bhai’ya (Shahidul Alam). It was in the Sonargaon Hotel. A huge, fancy affair, where we had trouble walking, where our feet kept slipping on the shiny lobby floor. A different world, the world of the rich. As if that wasn’t enough, Pintu had lost one of his sandals on the way there. We knew we wouldn’t be allowed inside in bare feet, but Bhai’ya told us that there was no need to worry, that everything would be fine. So we walked on that slippery floor and looked everywhere. Everything seemed so grand, everything smelled of money. People throw away so much money! In the middle of the hotel was a swimming pool with almost-naked foreigners in it. We felt too ashamed to look at them.
We remember the time we had to go to some UNICEF meeting or other with Bhai’ya (Shahidul Alam). It was in the Sonargaon Hotel. A huge, fancy affair, where we had trouble walking, where our feet kept slipping on the shiny lobby floor. A different world, the world of the rich. As if that wasn’t enough, Pintu had lost one of his sandals on the way there. We knew we wouldn’t be allowed inside in bare feet, but Bhai’ya told us that there was no need to worry, that everything would be fine. So we walked on that slippery floor and looked everywhere. Everything seemed so grand, everything smelled of money. People throw away so much money! In the middle of the hotel was a swimming pool with almost-naked foreigners in it. We felt too ashamed to look at them. When we go somewhere people usually comment ‘Oh you poor deprived children’. Nonsense! If they grab all the opportunities of course we’ll be deprived. First they take everything for themselves, then they coo ‘Oh, you poor deprived child’. If we are not given a chance, how can we make it? Our speech, the way we talk is offensive to the bhadrolok, the upper class. ‘Oooh, your pronunciation,’ they sniff at us, ‘the way your language wanders all over the place.’
When we go somewhere people usually comment ‘Oh you poor deprived children’. Nonsense! If they grab all the opportunities of course we’ll be deprived. First they take everything for themselves, then they coo ‘Oh, you poor deprived child’. If we are not given a chance, how can we make it? Our speech, the way we talk is offensive to the bhadrolok, the upper class. ‘Oooh, your pronunciation,’ they sniff at us, ‘the way your language wanders all over the place.’