rahnuma ahmed
As a little child, when I was only three or four, I couldn’t understand how people could still see me if I shut my eyes.
Later, like most people, I grew up. I realised shutting my eyes didn’t make me any less visible to others.
Reading the recently-published Human Rights Watch report, available on the internet, The Torture of Tasneem Khalil. How the Bangladesh Military Abuses Its Power under the State of Emergency reminded me of my childhood follies. And I thought, hmm no one talks of military torture. Police torture, yes. RAB torture, umm, maybe. If you are foolhardy. Or if you are Jahangir Alam Akash, an outspoken Rajshahi journalist (see his just-published Ondhokarey Ponero Ghonta).
But military torture. No. DGFI torture i.e., torture at the hands (or boots) of military intelligence. NEVER. Unless one is Professor Anwar Hossain (Jobanbondi, Kara Deenolipi).
Talking of torture by state agencies, against its own citizens… but no hold it. Is the DGFI a mere state agency? Don’t keener analysts, those who don’t regurgitate dead political theories on TV, say that it has come to represent a state within a state?
Torture doesn’t reveal the truth
It was a medieval idea, that pain had to be inflicted on the body for truth to pour out. The purpose of modern torture is different. To instill fear. To crush political dissent. To wreak havoc and destroy lives. Often performed out of sheer habit. To assert supremacy. To possess nations. To build empires anew. The ticking bomb theory seeks to justify torture. What if a bomb timed to detonate at the rush hour has been planted in a crowded metro area. What if security forces have been able to identify and pick up the terrorists. Surely, to save innocent lives…
But reality is more complex. Torture doesn’t bring out the truth. Torture victims have repeatedly said that after a certain point they admit to nearly anything. To stop the pain being inflicted. Unless one is Khaled Shaikh Mohammed, described by US intelligence agencies as a 9/11 operational planner. Khaled was waterboarded, a torture technique where the prisoner is made to feel as though he is drowning. The interrogators used both hot and cold water. He was subjected to all kinds of deprivations, beatings, threats. They failed. He won the grudging respect of his interrogators. The high point was when they threatened to harm his children — a boy and a girl, age 7 and 9 — also captured. Khaled replied, “That’s fine. You can do what you want to my children, and they will find a better place with Allah.” He did give his interrogators some information, but as CIA expert Ron Suskind says, they were things that professional interrogators could have gotten otherwise. CIA’s torture methods, says Suskind, are “unproductive.”
Many liberal democratic governments in the West are embarrassed at having to employ torture. The war on terror, the horrors at Abu Ghraib and Guantanamo have given rise to convoluted descriptions of what is torture, how to measure torture, levels of acceptable pain. Often enough one comes across public officials quibbling over the legality of particular forms of pain and suffering inflicted. For instance, the newly-appointed US Attorney General Michael Mukasey refused to comment on whether waterboarding constituted torture. In a letter to the Senate Judiciary Chairman, Mukasey wrote, “it is not an easy question.”
It’s funny how perceptions can change when questions are framed differently. “If I had water draining into my nose, oh God, I just can’t imagine how painful! Whether it’s torture by anybody else’s definition, for me it would be torture,” is what US national intelligence chief Mike McConnell said in a New Yorker magazine interview.
Do not forget me comrade
“I think I owe my resistance to a variety of concepts. Love is one of them. Poetry. Despair also, but not in the sense of suicide or surrender. Sadness was also present. There was also an ethical dimension. I was raised to be unbreakable, there was no choice but to resist,” said Syrian poet and journalist Faraj Ahmad Bayrakdar, to the Lebanese newspaper An Nahar. Faraj was imprisoned and tortured for his political activities and membership of the League of Communist Action. Termed one of the world’s “forgotten prisoners,” he was released from prison 14 months before the end of a 15-year jail sentence.
The most painful torture method, said Faraj, was the German chair. He calls it the “Nazi chair.” The prisoner is tied to a metal chair, it is then folded backwards, so that it pressurizes the back of the prisoner. Once put on that chair, any full breath can kill. “He has to calibrate his breathing on the edge of pain between two half-breaths. His life is placed on that line.” Once Faraj had to be carried back to his cell on a blanket. On the way, he had a vision of Malek Bin Arrayb when it was his time to die. “I felt the similarities between him and me. I didn’t fear death, I was only sad.” He composed this verse:
I wasn’t alive
And I wasn’t dead
So I made my way for him
Oh, how the narrowness of this place
Shames me.
For others, composing poetry while in prison has provided a feeling of control. It has defeated feelings of helplessness. Muriel Dockendorff Navarrete was 23 in 1974. A poet, lyricist, and economics student, she was arrested by the DINA in Santiago, Chile, for her organizing activities. Married a year ago, she was never again seen by her husband, or other members of her family. Muriel wrote this poem for “Sandra,” a fellow torture-center detainee, on the inside of a cigarette packet:
I remember when I met you in the house of terror, of what you gave me and surrendered to me.
In those moments in which the light was a dream or a miracle. However, you were the light amongst the darkness.
We were as one in our misfortune. Today, after thousands of
misfortunes more, I can see you, as I did then, always looking forward.
We will see each other again through the fog that we will disperse.
Do not forget me comrade.
It also leaves messages for us, for those outside. We must not forget. Neither Muriel, nor “Sandra.” Nor all others tortured. We must work to disperse the fog.
You are the law. You are God
Nufar Yishai-Karin, Israeli clinical psychologist at Hebrew University in Jerusalem, interviewed 21 Israeli soldiers. They confessed to assaulting Palestinians in the Gaza Strip and West Bank. Frequently. Brutally.
The majority of the interviewees confessed at some point or the other, that they “enjoyed [the] violence.” It broke the routine, they liked the destruction and the chaos. Violence and the sense of danger gave them a feeling of power.
One of the soldiers said, “The truth? When there is chaos, I like it. That’s when I enjoy it. It’s like a drug. If I don’t go into Rafah, and if there isn’t some kind of riot once in some weeks, I go nuts.” Another soldier explained: “The most important thing is that it removes the burden of the law from you. You feel that you are the law. You are the law. You are the one who decides… As though from the moment you leave the place that is called Eretz Yisrael [the Land of Israel] and go through the Erez checkpoint into the Gaza Strip, you are the law. You are God.”
According to Human Rights Watch, Tasneem’s account is “the most detailed public account of a
case of torture in Bangladesh.” There are other testimonies too. The truth has been told.
We can no longer keep our eyes shut.
New Age 18 Feb 2008
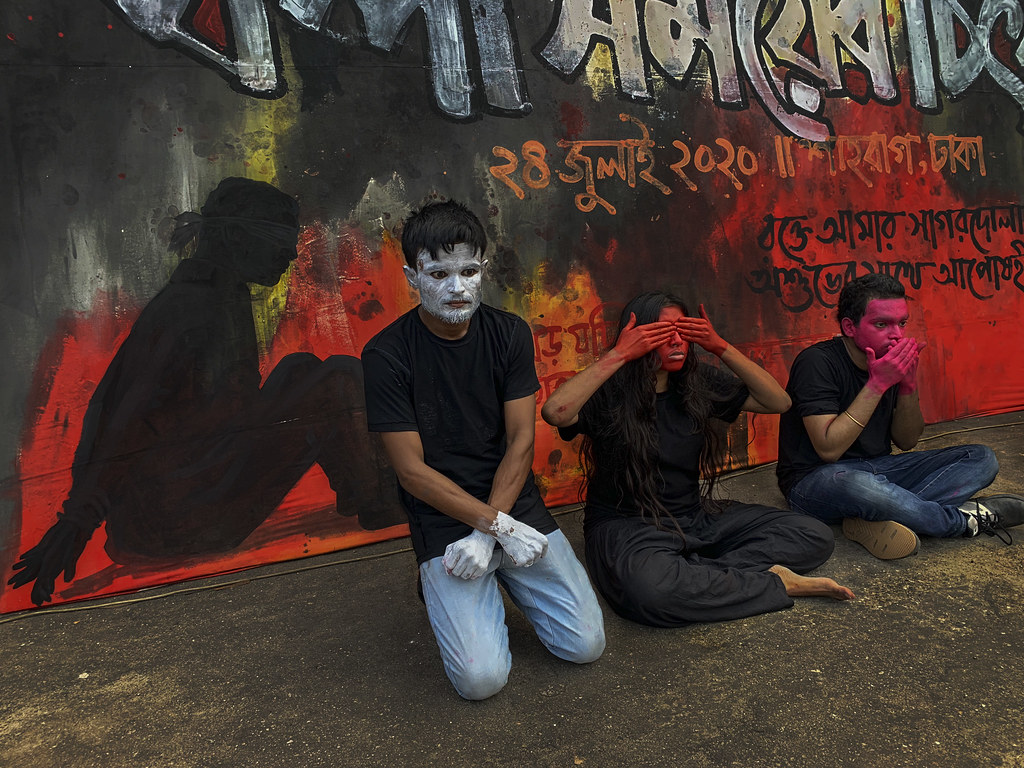

 Jyotirmay Guhathakurta and Basanti Guhathakurta with seven year old daughter, Meghna and nephew Kanti in Gandaria, Dhaka, 1966. Bangladesh.
Jyotirmay Guhathakurta and Basanti Guhathakurta with seven year old daughter, Meghna and nephew Kanti in Gandaria, Dhaka, 1966. Bangladesh.  Choles Ritchil. Photographer unknown
Choles Ritchil. Photographer unknown Mutilated body of Choles Ritchil. Photographer unknown
Mutilated body of Choles Ritchil. Photographer unknown Cleaners clearing debris outside the Rangs Building to make way for traffic. Early hours of the morning. 8th December 2007. Dhaka. Bangladesh. ? Zaid Islam
Cleaners clearing debris outside the Rangs Building to make way for traffic. Early hours of the morning. 8th December 2007. Dhaka. Bangladesh. ? Zaid Islam Demolition workers who have set up their own emergency team, warm themselves at night. 8th December 2007. Dhaka. Bangladesh.
Demolition workers who have set up their own emergency team, warm themselves at night. 8th December 2007. Dhaka. Bangladesh. 







