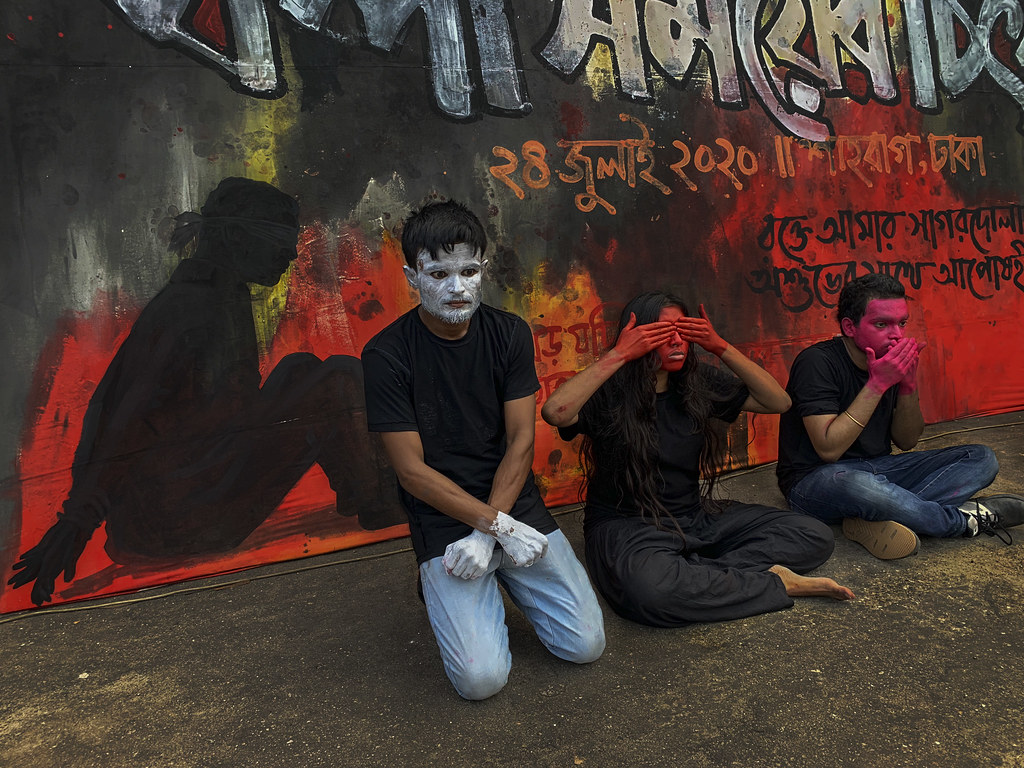Category: Oil
PART I: FIFTY-NINTH ANNIVERSARY OF CIA-MI6 COUP
Remembering Mosaddeq
by?rahnuma ahmed

The anniversary’s just around the corner, for the regime of Dr Mohammad Mosaddeq — popular and democratically-elected prime minister of Iran — was toppled by the CIA-MI6 on August 19, 1953. The military coup returned the Shah of Iran, Mohammad Reza Pahlavi, to power. A brutal dictatorship, not acknowledged as such by the US, UK and other western powers because he had served their interests.
Media interest (both mainstream and alternative) in CIA involvement was revived with the publication of the CIA’s official history of the 1953 coup in The New York Times on April 16, 2000. Continue reading “PART I: FIFTY-NINTH ANNIVERSARY OF CIA-MI6 COUP”
The Lily-Pad Strategy
The first thing I saw last month when I walked into the belly of the dark grey C-17 Air Force cargo plane was a void — something missing. A missing left arm, to be exact, severed at the shoulder, temporarily patched and held together.? Thick, pale flesh, flecked with bright red at the edges. It looked like meat sliced open. The face and what remained of the rest of the man were obscured by blankets, an American flag quilt, and a jumble of tubes and tape, wires, drip bags, and medical monitors.
That man and two other critically wounded soldiers — one with two stumps where legs had been, the other missing a leg below the thigh — were intubated, unconscious, and lying on stretchers hooked to the walls of the plane that had just landed at Ramstein Air Base in Germany. A tattoo on the soldier?s remaining arm read, ?DEATH BEFORE DISHONOR.?
Continue reading “The Lily-Pad Strategy”
Big Oil Buys Senate To Protect Government Subsidies
Looks as if the same game is played all over the globe!
Not for art's sake

Abstract of keynote presentation given at National University of Taiwan
8th January 2012. Taipei
Subscribe to ShahidulNews
One of the videos presented. A compilation from several videos on major protests in 2011
Long before CSR had become a buzzword and superstars and corporates began to find it essential to have pet social causes to support, we had set up Drik, a small organisation in Bangladesh, which made social justice its raison d’?tre.
Over two decades later, when my show on extra judicial killings at the gallery of Drik, was interpreted by a group of international curators as a ?fantastic performance?. It was time for me to take stock, and see where the art world situated itself and whether I belonged to this marketplace.
As collective movements go, the sub-continent has had its share. Colonial rule, oppression by the landed gentry, women?s struggle for equality in a patriarchal society and the injustice of caste have all been challenged. The solidarity of sustained groups, often against overwhelmingly stronger entities with far greater resources. had been a trademark for undivided India and for Bengal in particular.
It was the dynamics of a ruling class propped up by local agents who stood to profit from inequality, that led to the Gandhian strategy of non-violent resistance. Other methods had also been tried, and Subhas Chandra Bose, with a much more militant outlook, also had a huge following. The Tebhaga peasant movement by the Kisan Sabha had led to laws being formulated that limited the share of the landlords.
Partition did not cure these ills. The ouster of the British did not break up the class structure, but replaced one set of exploiters with another. The British, and other imperial powers continued to maintain unequal trade relations, sometimes in the guise of aid.
Cultural activists in Bangladesh had operated within this milieu. With the military under the control of the West wing, the more populous East Pakistan felt the weight of oppression. Military rule became the vehicle for continued repression but failed to quell the unrest and even the final genocidal attack on the people of East Pakistan, was repulsed by a countrywide resistance.
An independent Bangladesh, free of foreign occupiers, should have been a land free of repression. The reality was very different and cultural activists have had to find new ways of resistance. This has required documentation, articulation and tools of creative expression to deal with injustice in many forms. Having been failed by the major political parties (both government and opposition), cultural actors formed their own groups. Operating with minimum resources, we devised numerous initiatives to mobilise public opinion. Using both new and traditional media, as well as the networking ability of social media we formed lean and tenacious campaigns that chipped away at the establishment and its cohorts insisting on being heard and bent on achieving justice.
But the corporatization of modern Bangladesh has brought about many changes. I remember as a child that we used to respond to natural disasters by grouping together, singing songs, raising money, collecting food and old clothes and going out to affected areas to distribute them. We now leave such activities to the NGOs. Social movements are now sponsored by multinationals and protesters in rallies have sunshades parading the brand logos of telecom companies.
We had simultaneously taken on the hegemony of the west and its new southern accomplices, as well as the repressive regimes that operated within the nation state. But today we also need to examine how social movements have been appropriated, and our inability to operate without ?funding? regardless of the cause seriously limits our capacity for social and political intervention.
As an artist, as an activist, and as an organizer, I have along with my colleagues taken on technology, art, education and culture in its diverse forms and have presented a cohesive front that has challenged the military, major political parties and corporates, while continuing to operate independently within public and private spheres.
The presentation attempts to show how, by resisting not only the formal entities that have usurped power, but also the cultural norms that attempt to pigeon-hole cultural practice in terms of ?fine art?, I as an individual artist, as well as worker in a commune, have tried to ensure that our ?art? does not limit itself to admiration in a gallery. It breathes the gunpowder laden air of street battles with police, the dank vapours of the factory floor and pervades the silence of patriarchal inner chambers.
Shahidul Alam
8th January 2012
Taipei
Dead men tell no tales
Subscribe to ShahidulNews
By Vijay Prashad
21 October 2011 ??The Greanville Post ? Qaddafi, From Beginning to End
NATO?s Agenda for?Libya
 On the dusty reaches out of Sirte, a convoy flees a battlefield. A NATO aircraft fires and strikes the cars. The wounded struggle to escape. Armed trucks, with armed fighters, rush to the scene. They find the injured, and among them is the most significant prize: a bloodied Muammar Qaddafi stumbles, is captured, and then is thrown amongst the fighters. One can imagine their exhilaration. A cell-phone traces the events of the next few minutes. A badly injured Qaddafi is pushed around, thrown on a car, and then the video gets blurry. The next images are of a dead Qaddafi. He has a bullet hole on the side of his head.
On the dusty reaches out of Sirte, a convoy flees a battlefield. A NATO aircraft fires and strikes the cars. The wounded struggle to escape. Armed trucks, with armed fighters, rush to the scene. They find the injured, and among them is the most significant prize: a bloodied Muammar Qaddafi stumbles, is captured, and then is thrown amongst the fighters. One can imagine their exhilaration. A cell-phone traces the events of the next few minutes. A badly injured Qaddafi is pushed around, thrown on a car, and then the video gets blurry. The next images are of a dead Qaddafi. He has a bullet hole on the side of his head.
These images go onto youtube almost instantly. They are on television, and in the newspapers. It will be impossible not to see them.
The Third Geneva Convention (article 13): ?Prisoners of war must at all times be protected, particularly against acts of violence or intimidation and against insults and public curiosity.?
The Fourth Geneva Convention (article 27): ?Protected persons are entitled, in all circumstances, to respect for their persons, their honor, their family rights, their religious convictions and practices, and their manners and customs. They shall at all times be humanely treated, and shall be protected especially against all acts of violence or threats thereof and against insults and public curiosity.?
One of the important ideological elements during the early days of the war in Libya was the framing of the arrest warrant for Qaddafi and his clique by the International Criminal Court?s selectively zealous chief prosecutor Luis Moreno Ocampo. It was enough to have press reports of excessive violence for Moreno Ocampo and Ban Ki-Moon to use the language of genocide; no independent, forensic evaluation of the evidence was necessary. [Actually, independent evaluation was soon forthcoming from Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch, decisively debunking Ocampo?s charges. AC/JSC.]
NATO sanctimoniously said that it would help the ICC prosecute the warrant (this despite the fact that the United States, NATO?s powerhouse, is not a member of the ICC). This remark was echoed by the National Transitional Council, NATO?s? political instrument in Benghazi.
Humanitarian intervention was justified on the basis of potential or alleged violations of the Geneva Conventions. The intervention?s finale is? a violation of those very Conventions.
It would? have been inconvenient to see Qaddafi in open court. He had long abandoned his revolutionary heritage (1969-1988), and had given himself over to the U. S.-led War on Terror at least since 2003 (but in fact since the late 1990s). Qaddafi?s prisons had been an important torture center in the archipelago of black sites utilized by the CIA, European intelligence and the Egyptian security state. What stories Qaddafi might have told if he were allowed to speak in open court? What stories Saddam Hussein might have told had he too been allowed to speak in an open court? As it happens, Hussein at least entered a courtroom, even as it was more kangaroo than judicial.
No such courtroom for Qaddafi. As Naeem Mohaiemen put it, ?Dead men tell no tales. They cannot stand trial. They cannot name the people who helped them stay in power. All secrets die with them.
Qaddafi is dead. As the euphoria dies down, it might be important to recall that we are dealing with at least two Qaddafis. The first Qaddafi overthrew a lazy and corrupt monarchy in 1969, and proceeded to transform Libya along a fairly straightforward national development path. There were idiosyncrasies, such as Qaddafi?s ideas about democracy that never really produced institutions of any value. Qaddafi had the unique ability to centralize power in the name of de-centralization. Nevertheless, in the national liberation Qaddafi certainly turned over large sections of the national surplus to improve the well-being of the Libyan people. It is because of two decades of such policies that the Libyan people entered the 21st century with high human development indicators. Oil helped, but there are oil nations (such as Nigeria) where the people languish in terms of their access to social goods and to social development.
By 1988, the first Qaddafi morphed into the second Qaddafi, who set aside his anti-imperialism for collaboration with imperialism, and who dismissed the national development path for neo-liberal privatization (I tell this story in Arab Spring, Libyan Winter, which will be published by AK Press in the Spring of 2012). This second Qaddafi squandered the pursuit of well-being, and so took away the one aspect of his governance that the people supported. From the 1990s onward, Qaddafi?s regime offered the masses the illusion of social wealth and the illusion of democracy. They wanted more, and that is the reason for the long process of unrest that begins in the early 1990s (alongside the Algerian Civil War), comes to a head in 1995-96 and then again in 2006. It has been a long slog for the various rebellious elements to find themselves.
The new leadership of Tripoli was incubated inside the Qaddafi regime. His son, Saif al-Islam was the chief neoliberal reformer, and he surrounded himself with people who wanted to turn Libya into a larger Dubai. They went to work around 2006, but were disillusioned by the rate of progress, and many (including Mahmud Jibril, the current Prime Minister) had threatened to resign on several occasions. When an insurengy began in Benghazi, this clique hastened to join them, and by March had taken hold of the leadership of the rebellion. It remains in their hands.
What is being celebrated on the streets of Benghazi, Tripoli and the other cities? Certainly there is jubilation at the removal from power of the Qaddafi of 1988-2011. It is in the interests of NATO and Jibril?s clique to ensure that in this auto-da-f? the national liberation anti-imperialist of 1969-1988 is liquidated, and that the neoliberal era is forgotten, to be reborn anew as if not tried before. That is going to be the trick: to navigate between the joy of large sections of the population who want to have a say in their society (which Qaddafi blocked, and Jibril would like to canalize) and a small section that wants to pursue the neoliberal agenda (which Qaddafi tried to facilitate but could not do so over the objections of his ?men of the tent?). The new Libya will be born in the gap between the two interpretations.
The manner of Qaddafi?s death is a synecdoche for the entire war. NATO?s bombs stopped the convoy, and without them Qaddafi would probably have fled to his next redoubt. The rebellion might have succeeded without NATO. But with NATO, certain political options had to be foreclosed; NATO?s member states are in line now to claim their reward. However, they are too polite in a liberal European way to actually state their claim publically in a quid-pro-quo fashion. Hence, they say things like: this is a Libyan war, and that Libya must decide what it must do. This is properly the space into which those sections in the new Libyan power structure that still value sovereignty must assert themselves. The window for that assertion is going to close soon, as the deals get inked that lock Libya?s resources and autonomy into the agenda of the NATO states.
VIJAY PRASHAD?is the George and Martha Kellner Chair of South Asian History and Director of International Studies at Trinity College, Hartford, CT His most recent book,?The Darker Nations: A People?s History of the Third World,?won the Muzaffar Ahmad Book Prize for 2009. The Swedish and French editions are just out. He can be reached at:?vijay.prashad@trincoll.edu
Police brutality
Subscribe to ShahidulNews
![]()
By rahnuma ahmed
Two hartals, in quick succession. During both, police forces deployed were brutal, as the photos reveal.
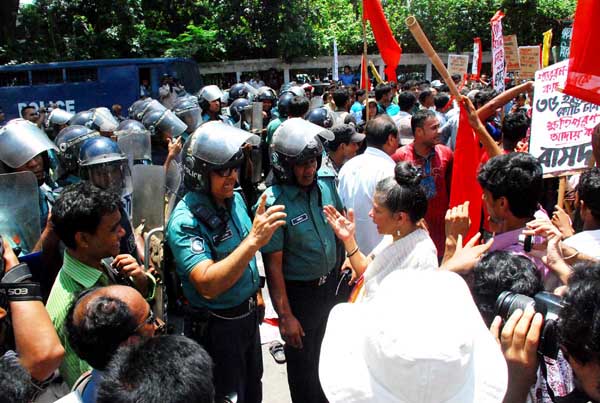
The similarity ends there, because the hartal called by the National Committee on Protection of Oil, Gas and Mineral Resources, Power and Ports was for 6 hours (July 3). It was called in protest against the government’s contract with ConocoPhillips signed on June 16; the deal awarded gas exploration and extraction rights to the US energy giant in two deep sea blocks in the Bay of Bengal. The National Committee’s demand? That the deal should be scrapped because it allows Bangladesh to have only 20% of the gas, it permits the company to export the remaining 80%. ?That under these conditions, the deal?similar to other deals signed by the government with multinational companies?goes against the national interest.

The hartal called by the Bangladesh Nationalist Party and its allies, for 48 hours (eight times more, July 6-7), was in protest against the recent 15th amendment of the constitution which includes scrapping the provision for a caretaker government?under which parliamentary elections are held?a one-and-half decade long practise in Bangladesh. Both major political parties are prone to shifting their position 180 degrees on the caretaker government issue depending on whether they are in, or out of, power. There is no credible reason to think that the Awami League would have assented to the scrapping if it had been in the opposition. Or, to forget the long drawn-out maneuverings of the BNP-Jamaat led government many months before national elections were due in 2007, ones that were calculated to ensure fool-proof rigging. In other words, to lead to the BNP-Jamaat led government’s re-election.

As Nurul Kabir insists, the nation is held hostage because the two major political parties have not been able to work out the `rules of the game,’ i.e., the elementary fact that at the end of its term the ruling government must necessarily hold free, fair and credible parliamentary elections, that it should have the political maturity to accept the people’s verdict. No doubt difficult, because each ruling party knows without a single trace of doubt?even though it is loath to admit it publicly?that the people’s verdict will throw it out of power. Because of its miserable 5 year performance. Because of reneging on its own electoral pledges.
Continue reading “Police brutality”
Rahnuma asks: Who is foreign agent, Anu Muhammad or Tawfiq Elahi?
Subscribe to ShahidulNews
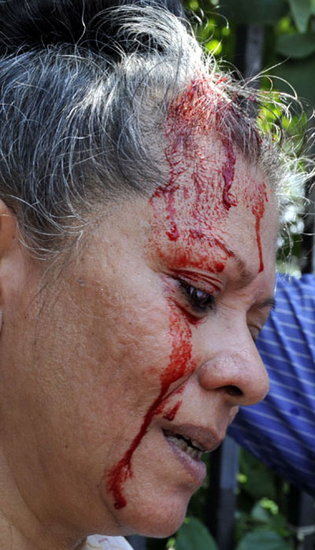
DHAKA: Renowned writer, researcher and activist Rahnuma Ahmed asks who is a ?foreign agent?, Anu Muhammad, member-secretary of the National Committee to Protect Oil, Gas, Mineral Resources, Power and Ports, or Dr. Tawfiq-e-Elahi Chowdhury, advisor to the Prime Minister on energy affairs?
Rahnuma was talking to banglanews24.com in an exclusive interview against the backdrop of the National Oil and Gas Committee`s siege of the energy ministry on June 14, 2011, police prevented the seige from taking place, Rahnuma was injured in clashes when police resorted to clubbing and lathi charge.
She raised this question when asked about the recent comments made by Dr. Hasan Mahmud, state minister for environment and forest, in the parliament about the oil and gas national committee, and about Anu Muhammad in particular.
Dr Hasan Mahmud told lawmakers, Anu Muhammad is a ?foreign agent,? and that the Oil and gas Committee was formed by `tokais` (street urchins) after the committee called a half-day hartal on July 3 in protest against the deal inked between the government and the US-based company ConocoPhillips for offshore oil and gas exploration. The contract includes the provision of gas export.
banglanews24.com?s Output Editor Mahmood Menon took the interview.
banglanews: Why do you think Bangladesh should not export its oil and gas?
rahnuma ahmed: I will mention only one reason because of space and time constraints, but before that I want to draw your attention to a basic issue. Natural energy resources are limited. They are non-renewable. They get depleted. And that`s why it`s essential that these should be made use of in a planned manner, that we need to seriously consider the issue of national reserves, our needs, how the national interest can best be secured, you know, these matters, that policies and plans of action should be well-thought out, well-planned.? Let`s talk of gas, national reserves are estimated to be 7.3 trillion cubic foot. According to the latest estimates, the daily shortfall of national energy needs is 450 million cubic foot. The demand for gas is increasing at an annual rate of 10%. According to government forecasts, gas reserves are likely to run out by 2014-2015. This is the picture. Continue reading “Rahnuma asks: Who is foreign agent, Anu Muhammad or Tawfiq Elahi?”
Rahnuma Ahmed Injured
Subscribe to ShahidulNews
Rahnuma Ahmed was amongst around twenty people who were injured as police clashed with protesters at a rally held near the National Press Club in Dhaka on 14th June 2011.
Members of the National Committee to Protect Oil, Gas, Mineral Resources, Power and Ports were protesting against the government bid to give lease of two deep-sea blocks to US oil company ConocoPhillips South Asia New Venture Ltd for oil-gas exploration in the Bay of Bengal, which they say is against the interest of Bangladesh and is designed to profit a few corrupt individuals.
The police blockaded the rally near the secretariat, and baton charged the protesters as they approached the barricade. Writer and anthropologist Rahnuma Ahmed was one of several protesters who were injured during the clashes. The government plans to sign a contract with Connoco Phillips on the 16th June 2011.


WikiLeaks cables: Bangladesh Gas
Subscribe to ShahidulNews
US nudged Bangladesh to allocate gas blocks
BS Reporter / New Delhi December 25, 2010, 0:15 IST
Every time India would ask Bangladesh for rights to explore gas, Dhaka would say the country had to first find if there was gas available at offshore locations. For the last one year, the issue hasn?t even been mentioned in discussions with Bangladesh, top petroleum ministry officials said. But India?s loss has been the US gain and it managed to walk away with the prize.
WikiLeaks tapes released late last night revealed how US-based ConocoPhillips was selected from a field of seven bidders and awarded two offshore blocks for exploring gas in 2009. The company was awarded a production sharing contract, with a provision to export the gas in the form of liquefied natural gas in the untapped areas of the Bay of Bengal. The bidders had agreed to stay away from disputed waters in the Bay of Bengal, something US Ambassador to Bangladesh, James Moriarty mentioned in his cables sent in July 2009. Conoco got the contract in October 2009.
Moriarty met Bangladesh Prime Minister Hasina Wajed?s energy adviser, Tawfiq Elahi Chowdhury, and got him to assure that ConocoPhillips would be awarded two of the uncontested blocks and Chevron given permission to go ahead with the first of the three compressors necessary to improve flow in Bangladesh?s main gas pipeline. Within three months, the Bangladesh government complied.
Defending themselves against the charge that they had allowed the US to have an advantage by not being proactive themselves, Indian Petroleum Ministry officials said Indian finds of gas had reduced the pressure to secure gas from Bangladesh.
WikiLeaks tapes also revealed that Moriarty urged Chowdhury to approve plans by British company Global Coal Management (GCM) to begin open-cast coal mining in the country?s Phulbari area. In the cable, Moriarty quoted Chowdhury saying the coal mine was ?politically sensitive in the light of the impoverished, historically oppressed tribal community residing on the land?.
The energy advisor, however, agreed to build support for the project through the parliamentary process, Moriarty said in the cable.
In a cable posted by WikiLeaks that was sent in July last year, Moriarty said he had urged Chowdhury to authorise coal mining, adding ?open-pit mining seemed the best way forward?. Later on in the cable, Moriarty said, ?Asia Energy, the company behind the Phulbari project, has 60 per cent US investment. Asia Energy officials told the ambassador they were cautiously optimistic that the project would win government approval in the coming months.?
The ?Phulbari killings? as they are known took the lives of three boys in 2006 when police fired at a demonstration near the mine site. Asia Energy?s shares had crashed in the international market as a result and the company had to undergo a brand change, including a name changing.
In the WikiLeaks cables, Moriarty?s conversations with Indian ambassador Pinaki Ranjan Chakravatry, by contrast, revealed no discussions of a commercial nature, only a general approval by India of the change in government in Bangladesh and US endorsement of a joint South Asian task force on counterterrorism.
India?s high commissioner in Dhaka obligingly told the US ambassador that while India would ?prefer a primarily bilateral engagement?, Bangladesh might want a regional force for political reasons ? allegations that she was too close to India.
Chakravarty spoke of Bangladesh?s keenness to ?invest heavily in Bangladesh?s moribund railway system? including reconnecting the Bangladeshi railroad system to Agartala in Tripura. He said Indian companies would be interested in setting up power plants in Bangladesh, though the price of electricity ?is still under negotiation?. The US takeaway from the conversation is that regional counter-terrorism cooperation would help US assets enormously. Much of the rest is yet to become a reality