Tag: rural
Bangladeshi blog Infolady wins Global Media Forum Award
This year’s Global Media Forum Award went to the project Infolady from Bangladesh. Finalists in the category addressed issues tied to the Deutsche Welle Global Media Forum 2013, which looks at “The Future of Growth – Economic Values and the Media.” The Infolady project helps equip women with digital cameras, mobile phones and solar-powered laptops to travel by bike to rural areas and answer questions related to health, agriculture and development. “Infoladies brings life-saving information about health, education and a number of other services to the poorest people in Bangladesh,” the jury said.

Continue reading “Bangladeshi blog Infolady wins Global Media Forum Award”
Coping With Life
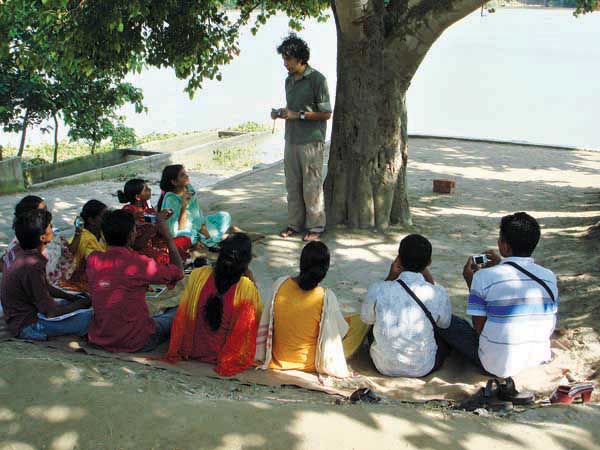 Practical session under a banyan tree on the banks of the river Mahananda, Chapainawabgonj. ? Reza/Drik
Practical session under a banyan tree on the banks of the river Mahananda, Chapainawabgonj. ? Reza/Drik
?Kamera tulen?. Elsewhere, one would think a hundred times before pointing a camera. Permission, legality, issues of representation, all came into play. In any Bangladeshi village, getting people out of your lens is the problem. A cluster of heads surround the LCD. Peals of laughter. Old toothless smiles, a little baby held up so she can see. The disappointment of being left out. There might be serious issues to be dealt with, but right now being photographed was all that mattered.
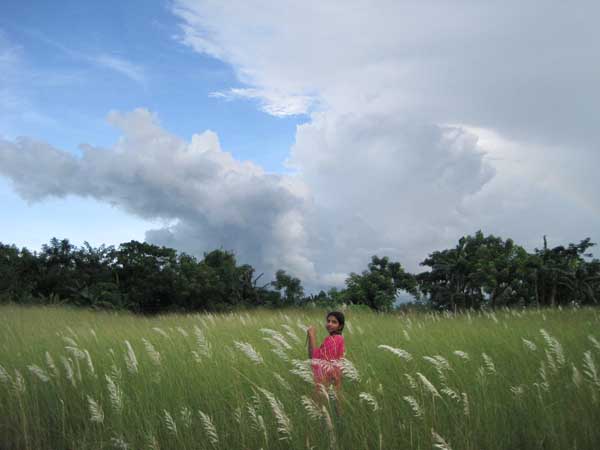 Fourteen-year-old Rabeya, a member of our adolescent group, was taking photos in this beautiful location. I want everyone to live in such a beautiful environment. Jamalpur, 2009. ? Fatema Akter Hasi; 14
Fourteen-year-old Rabeya, a member of our adolescent group, was taking photos in this beautiful location. I want everyone to live in such a beautiful environment. Jamalpur, 2009. ? Fatema Akter Hasi; 14
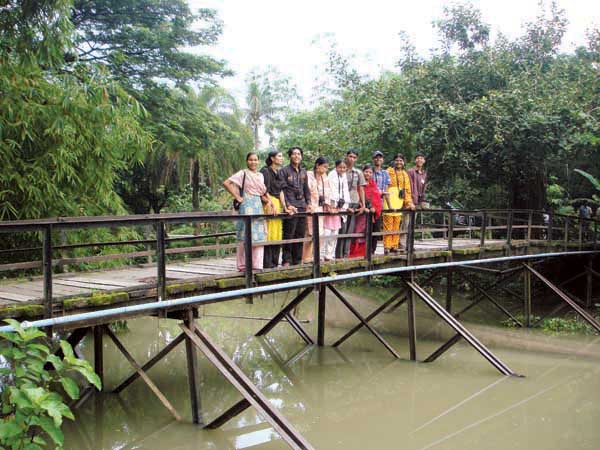 Trainees from?Barguna. ? Jeevani Fernando
Trainees from?Barguna. ? Jeevani Fernando
With every intervention, one has concerns. Entering people?s lives, creating expectations, making friends, all have to deal with the disengagement that follows. It was people you were dealing with. How do you walk out of a life you have changed, perhaps forever? What do you leave behind, how much do you take away? These were difficult questions and we didn?t really have answers. But we?d tried it before, in cities and in villages. The remarkable transformations it had made to some children?s lives made the risk worth taking.
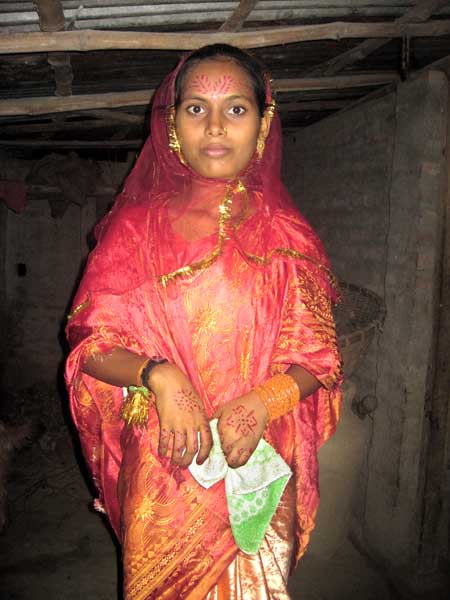 This is Shorifa Begum on her wedding day in Taherpur. She is a bride at eighteen years old. Shorifa did not want to get married. She stopped her education because she could not afford to continue it. Then her mother forced her to get married to a man who agreed to have a cheap wedding ceremony. Chapainawabgonj, 2009. ??Morium Khatun; 16
This is Shorifa Begum on her wedding day in Taherpur. She is a bride at eighteen years old. Shorifa did not want to get married. She stopped her education because she could not afford to continue it. Then her mother forced her to get married to a man who agreed to have a cheap wedding ceremony. Chapainawabgonj, 2009. ??Morium Khatun; 16
 Md. Moinuddin training in Jamalpur. ? Aminuzzaman/Drik
Md. Moinuddin training in Jamalpur. ? Aminuzzaman/Drik
There were aesthetic concerns too. In talking of composition, rules of thirds, moments, balance, were we suppressing their spontaneity? Did we impinge upon their way of seeing? Were we erasing their natural ability to tell stories? We needn?t have worried. Sure, they tried things out. Pictures were created with remarkable composition. Balanced frames with well-placed elements formed stylised images that a trained photographer would have been proud of, but we had underestimated their instincts. Our fears of over intrusion were unfounded. The most striking images resulted not from our training, but because they had a voice. They could now tell their own stories and no one was going to get in their way, not even their teachers. The proud, chest-out, stiff at attention pose, that thwarted every photographer looking for something ?natural? was very much part of that expression. The loud coloured d?cor that would embarrass the urban genteel, was shown off with panache. Quirky images of everyday scenes, seen the way only children see, were the nuggets that glittered through our light box.
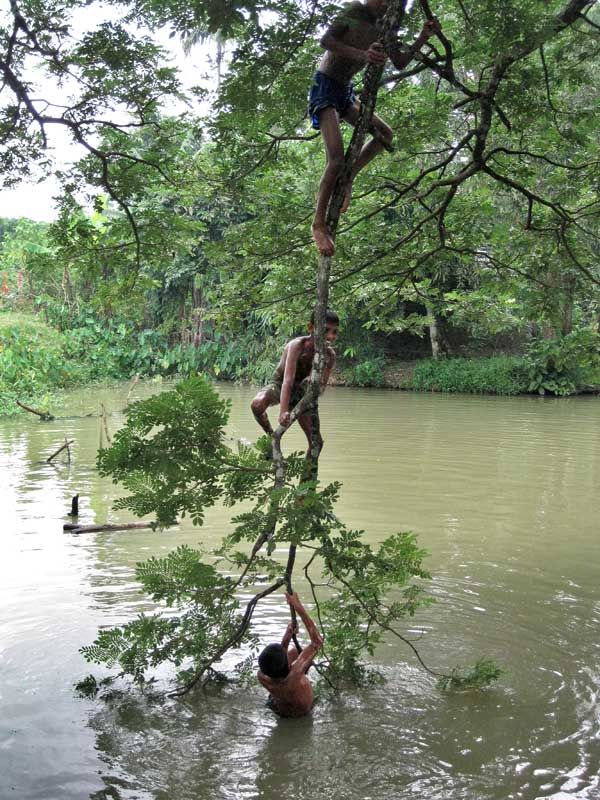 A group of children play in a local pond by climbing onto the tree and jumping into the water. They don’t go to school as their fathers are rickshaw pullers and do not earn enough to educate them. The parents are also not fully aware of the value of education. Barguna, 2009. ??Mohammad Jashim Uddin; 18
A group of children play in a local pond by climbing onto the tree and jumping into the water. They don’t go to school as their fathers are rickshaw pullers and do not earn enough to educate them. The parents are also not fully aware of the value of education. Barguna, 2009. ??Mohammad Jashim Uddin; 18
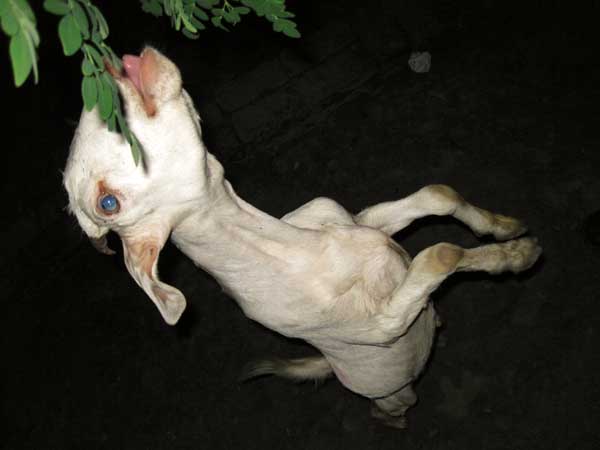 This is my uncle Shahidul’s goat. Every evening my uncle plays with the goat by holding up a leafy branch for him to jump up and eat. I watched this and took a photo. I also think that if the goat could become a human, then it might not need to jump like this. Chapainawabgonj, 2009. ? Md. Sala-uddin Ahmed; 16
This is my uncle Shahidul’s goat. Every evening my uncle plays with the goat by holding up a leafy branch for him to jump up and eat. I watched this and took a photo. I also think that if the goat could become a human, then it might not need to jump like this. Chapainawabgonj, 2009. ? Md. Sala-uddin Ahmed; 16
There were quiet reflective moments too. Their realities, the every day challenges, the matter of factness with which they dealt with hurdles, had an immediacy that would humble a trained professional. Layered between romantic images in fields of Kash, looming clouds over flowing rivers, coiled branches silhouetted against stormy skies, were photographs that talked of strife. People less able who insisted on being able. Children longing to be children. A much too young bride. Another young mother to be, gingerly treading through a treacherous path. Absent are the images they were not allowed to show. That threatened a patriarchal society?s image. Pictures they had been forced to delete. Pictures they had staged, as their reality was being suppressed. To delete, to stage, to deal with censorship. These are things they hadn?t been taught. They were learning on the fly. Dealing with situations as best as they could. They were coping with life. Perhaps the ultimate lesson.
Shahidul Alam
Dhaka
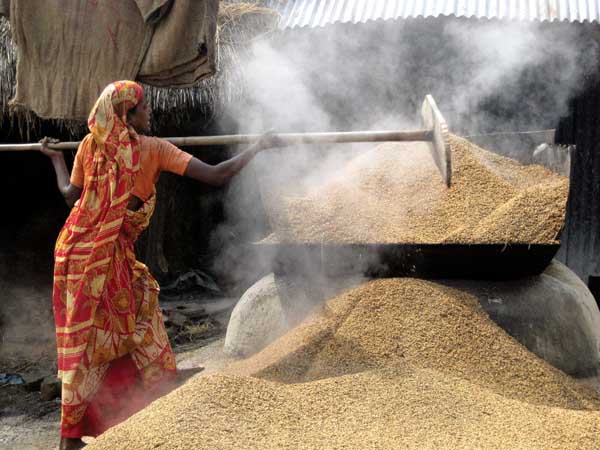 This woman is removing paddy from the basket after it is boiled. She keeps her feet on a jute bag so that they don’t get burnt. Barguna, 2009. ? Tania Islam Jhuma; 14
This woman is removing paddy from the basket after it is boiled. She keeps her feet on a jute bag so that they don’t get burnt. Barguna, 2009. ? Tania Islam Jhuma; 14
 Nature photographer. ? Reza/Drik
Nature photographer. ? Reza/Drik
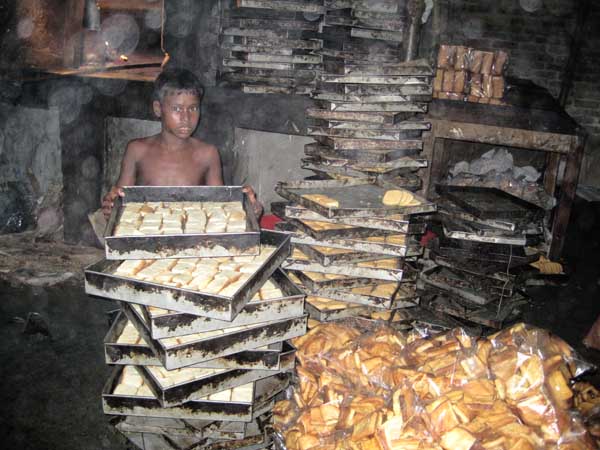 Sohel, 12, lives in Nandina and works in Mostafa Bakery making biscuits and other snacks. He helps his family with his daily wages. It amazes me that a young boy like Sohel has to work for a living instead of going to school. I do not want any child to work for a living. We have to create awareness among people about child labour. Jamalpur, 2009. ? Md. Amir Hossain Apon; 14
Sohel, 12, lives in Nandina and works in Mostafa Bakery making biscuits and other snacks. He helps his family with his daily wages. It amazes me that a young boy like Sohel has to work for a living instead of going to school. I do not want any child to work for a living. We have to create awareness among people about child labour. Jamalpur, 2009. ? Md. Amir Hossain Apon; 14
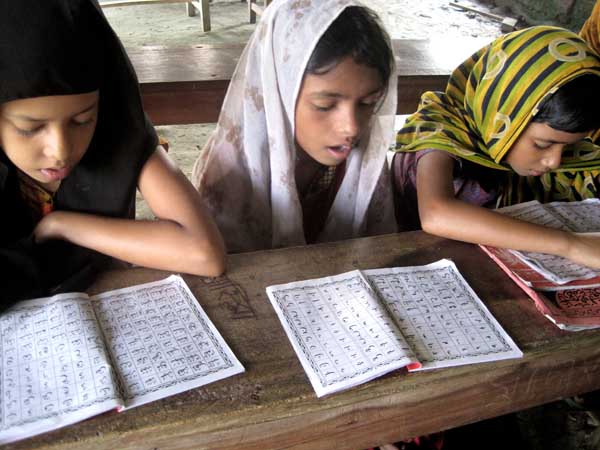 Amy and Rumi are 11 and 12 years old. They go to the madrasa to learn Arabic every morning. Barguna, 2009. ? Tania Islam Jhuma; 14
Amy and Rumi are 11 and 12 years old. They go to the madrasa to learn Arabic every morning. Barguna, 2009. ? Tania Islam Jhuma; 14
Chalking up Victories
Subscribe to ShahidulNews
At 17 Mozammat Razia Begum is older than most of the girls in her class at the Narandi School. She was married at 15 but her husband abandoned her.
?If I had been educated he would not have been able to abandon me so readily, leaving me nothing for maintenance,? she says. The marriage of young girls without proper contracts – followed soon after by abandonment – is a serious social problem in Bangladesh. Razia blames her parents. ?My parents were wrong to marry me off so young. If I had a daughter, I should not let her marry until she was at least 19.?
The school Razia attends is one of 6,000 non-formal village schools set up by BRAC – the Bangladesh Rural Advancement Committee – exclusively for pupils who have never started school and those who had to drop out. Three-quarters of the 180,000 pupils are girls. Although married girls are not normally catered for, exceptions are made. Many of the teachers are women: parents in Bangladesh frequently keep their daughters away from school if teachers are male. And each BRAC school is situated right in the community: if schools are far away parents will not let girls attend. It is not acceptable for girls – especially those past puberty – to walk about the countryside in this devout Muslim country.
?I am fortunate to be here,? says Razia, looking round the schoolroom with its tin roof and walls of bamboo and mud. She had to fight to come, though. Her father believes that a woman?s place is at home. ?Had I been a boy,? she said, ?my father would surely have allowed me to study.?
Razia?s own mother was married at 12 and, like her oldest daughter, had no say in the matter. ?I want my sisters? lives to be different. They should study and be given a choice about their marriage. Husbands will not dare to treat an educated woman badly.? On this subject, Razia becomes quite animated.
Razia would like to go on with her studies after she has completed the BRAC course. During the two-and-a-half hour daily session – which is timetabled to fit in with seasonal work and religious obligations – she learns literacy and numeracy, as well as enjoying activities such as singing, dancing, games and storybook reading.
BRAC have had a remarkable success in keeping the drop-out rate from their schools to five per cent and graduating 90 per cent of their students into the formal primary system. This proves that the obstacles to girls? education – even in such a poor environment – can be overcome.
As for Razia, her experience of life has forced her to question many things she once took for granted – such as the need to get married. She does not wish to marry again. And many other girls have begun to question the restrictions imposed on them. More of them want to be teachers – like their own teacher – or doctors. Razia says: ?I tell my sisters to study well and get a job. If they get a job they will be able to do as well as men and men will respect them.?
First published in the New Internationalist Magazine in Issue 240